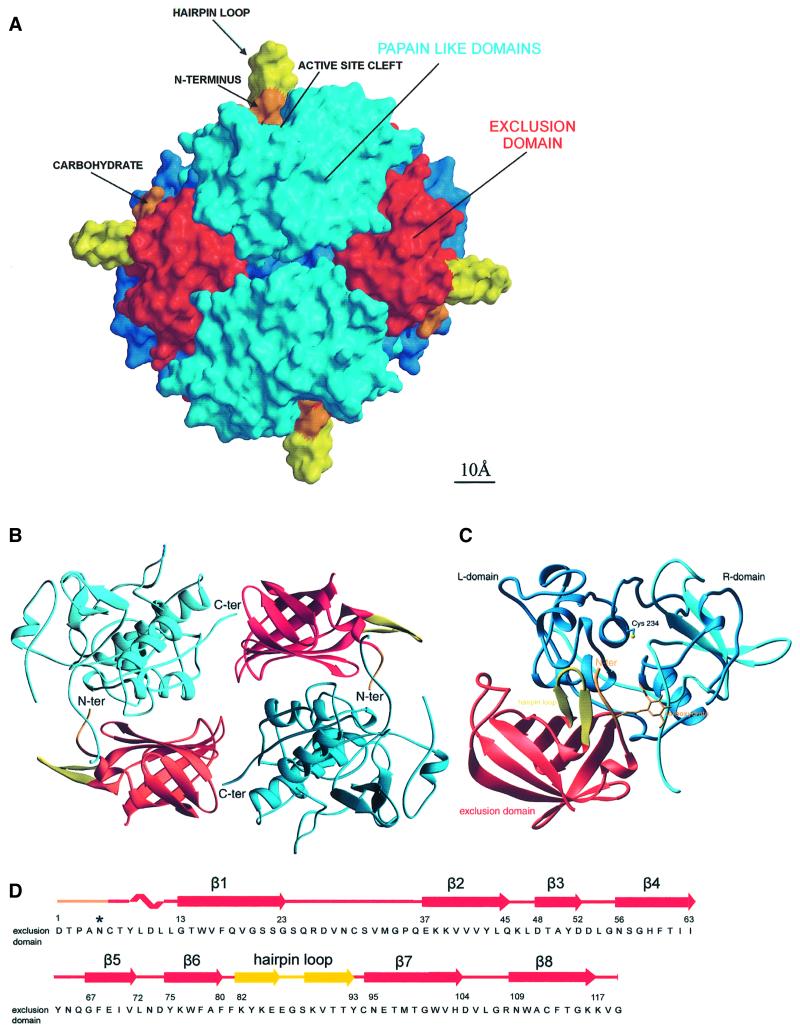
Fig. 1. Tetrahedral structure of DPPI. (A) Molecular surface of the tetrahedral structure of DPPI. The surface of papain-like domains is shown in blue, whereas the surface of exclusion domains is shown in red, orange and yellow. The view is along two active sites towards the exclusion domain hairpin loop (Lys82–Tyr93), shown in yellow, building a wall behind the active site cleft and five N-terminal residues, shown in orange. The left and right molecules are shown from the back towards the exclusion domain. The molecular surface was generated with GRASP (Nicholls et al., 1991); the figure was prepared in MAIN (Turk, 1992) and rendered with RENDER (Merritt and Bacon, 1997). (B) DPPI dimer. Head-to-tail arrangement of two pairs of papain-like and exclusion domains. Color coding is the same as in (A). The view is from the inside of the tetramer along the dimer 2-fold axis. The figure was created with RIBBONS (Carson, 1991). (C) Ribbon plot of the functional monomer of DPPI. The view shows the structure from the top, down the central α-helix. It is perpendicular to the view used in (A). The color coding is the same as in (A) except that here the heavy and light chains are shown in cyan and blue, respectively. The side chain of catalytic Cys234 and disulfides are shown with yellow sticks. The figure was created with RIBBONS (Carson, 1991). (D) Sequence of the exclusion domain with its secondary structure assignment.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.