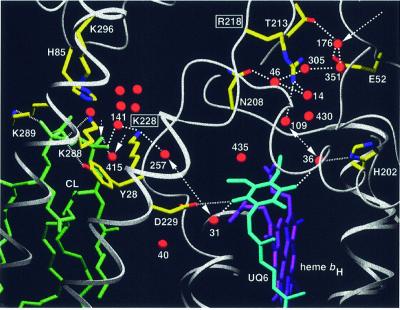
Fig. 7. Putative proton uptake pathways at the Qi site of yeast QCR via two arrays of hydrogen-bonded water molecules, which connect the bulk solvent at the matrix side with the site of ubiquinone reduction. The entrance to the E/R pathway is formed by Glu52 of QCR7 and Wat176. The gating residue towards the quinone-binding pocket is Arg218 of COB. Cardiolipin (L5) is positioned at the entrance to the CL/K pathway, for which Lys228 of COB is the gating residue. Arrows indicate the access sites from the bulk solvent, and double arrows show proton transfer between the key residues Arg218 or Lys228 of COB and UQ6. Side chains of amino acid residues that are involved in hydrogen bond interactions or ion pair formation are shown (standard colors). Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bond interactions. Dotted lines are used for hydrogen bond interactions of UQ6 and CL ligands (His202, Asp229 and Tyr28 of COB, and Lys288 and Lys289 of CYT1). Water molecules in the cavity above the cardiolipin headgroup are stabilized by interactions with side chains of Lys228 of COB, Lys296 of CYT1 and His85 of QCR7. A surrounding layer of non-polar residues (not shown) encloses the water-filled cavity. Transmembrane helices are shown as ribbon presentation and other polypeptide backbones as rope presentation. UQ6, heme bH and CL are represented as stick models.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.