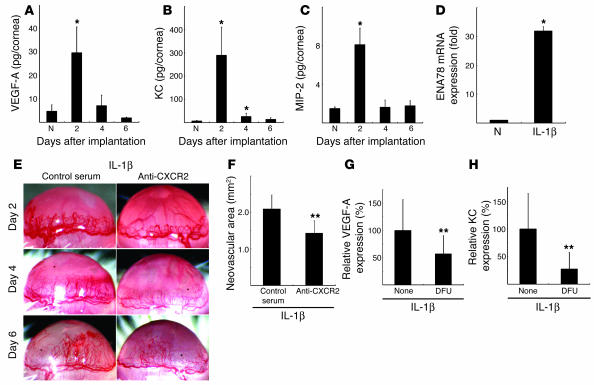
Figure 9.
The effect of anti-CXCR2 Ab on IL-1β–induced angiogenesis. Kinetics of protein expression for (A) VEGF-A, (B) KC (mouse CXCL1), and (C) MIP-2 (mouse CXCL2/3) after IL-1β pellet implantation. Four corneal lysates were prepared and assayed by ELISA on the indicated days (n = 3). *P < 0.01 versus untreated. (D) Expression of ENA-78 (CXCL5) mRNA levels in IL-1β–treated corneas. Six IL-1β–implanted corneas (IL-1β) or untreated corneas (N) were harvested, and real-time RT-PCR was performed to determine ENA-78 (CXCL5) mRNA levels on day 2. Expression was normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels. *P < 0.01 versus untreated. (E) Corneal neovascularization on days 2, 4, and 6 in BALB/c mice with or without i.p. administration of anti-mouse CXCR2 Ab. (F) Quantitative analysis of neovascularization on day 6. IL-1β–induced corneal neovascularization in mice (n = 6) receiving anti-mouse CXCR2 Ab was inhibited compared with mice (n = 6) receiving control goat serum. **P < 0.05 using Student’s t test. (G and H) Comparison of levels of VEGF-A (G) and KC (H) in IL-1β–implanted corneas with or without DFU. On day 4, corneal lysates were prepared from 4 IL-1β–implanted corneas from DFU-treated and untreated mice and individually assayed by ELISA for VEGF-A or KC (n = 3). **P < 0.05 using Student’s t test.