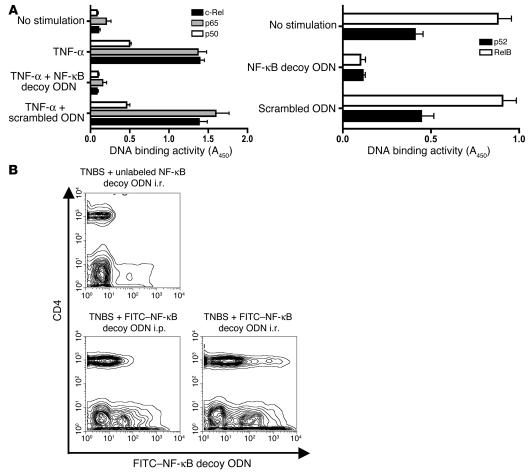
Figure 1.
Basic properties of NF-κB decoy ODNs. (A) Effect of NF-κB decoy ODNs on NF-κB DNA-binding activity. HeLa cells activated by TNF-α (20 ng/ml) or Raji cells (constitutively activated) were transfected with NF-κB decoy ODNs or scrambled ODNs encapsulated in a HVJ-E; 30 minutes after stimulation, the binding activity of p65, c-Rel, and p50 was determined in nuclear extracts of HeLa cells, whereas binding activity of Rel B and p52 was directly determined in nuclear extracts of Raji cells using the TransFactor assay. Data shown are mean values ± SD obtained from 2 independent experiments. Results are presented as absorbance at 450 nm (A450) wave length. (B) In vivo transfection of NF-κB decoy ODNs into CD4+ T cells and non-CD4+ T cells in the colonic lamina propria. Mice were administered FITC-conjugated NF-κB decoy ODNs (or unconjugated NF-κB decoy ODNs) i.r. 4 hours after TNBS administration or i.p. 4, 24, and 48 hours after TNBS administration; then, 5 days after TNBS-colitis induction, colonic lamina propria cells were isolated, stained with PE–anti-CD4, and analyzed by flow cytometry.