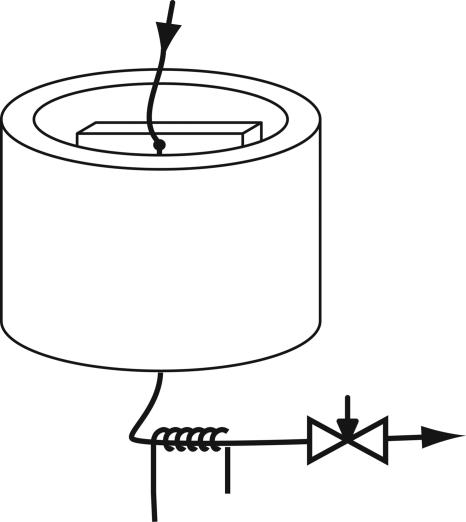
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup for flow and dispersion measurements. A pressurized hyperpolarized xenon gas mixture containing 0.3% NMR-active 129Xe [1% Xe at natural isotope abundance, 10% N2, and 89% He at 5.6 atm (1 atm = 101.3 kPa) of delivery pressure], spin-polarized to 10%, is supplied from the top. It flows via a capillary through the microfluidic device to be profiled and exits at the bottom. The entire microfluidic device is surrounded by an assembly of magnetic field gradient and rf coils (3 × 4.5 cm) for encoding, and the outlet capillary leads through a microsolenoid (3 mm long, 400-μm inner diameter) for remote signal detection. The flow rate is controlled by an adjustable constriction at the outlet. The whole apparatus is inserted into the bore of a superconducting magnet (7 T).