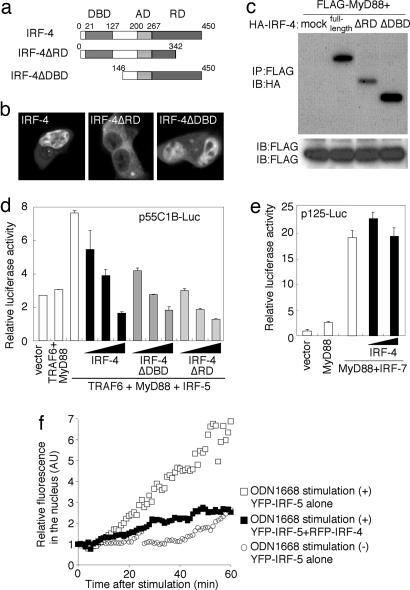
Fig. 3.
Negative regulation of the MyD88-dependent IRF-5 activation by IRF-4. (a) Schematic diagram of IRF-4-truncated mutants. DBD, DNA-binding domain; AD, activation domain; RD, regulatory domain (17, 20). (b) Confocal images of HEK293T cells transiently expressing YFP-IRF-4, YFP-IRF-4ΔDBD, or YFP-IRF-4ΔRD. (c) HEK293T cells were transfected transiently with the indicated combination of FLAG-tagged MyD88 and HA-tagged full-length IRF-4 or deletion mutants of IRF-4 and subjected to an immunoprecipitation assay. (d) The effect of IRF-4 expression on MyD88-TRAF6-dependent IRF-5 activation. HEK293T cells were transiently cotransfected with p55C1B-Luc and the expression vectors for the indicated combinations of MyD88 (25 ng), TRAF6 (25 ng), IRF-5 (25 ng), and full-length IRF-4 or mutants of IRF-4 (0, 1, 5, or 15 ng). Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after transfection. (e) The effect of IRF-4 expression on MyD88-dependent IRF-7 activation. HEK293T cells were cotransfected transiently with p125-Luc and the expression vectors for the indicated combinations of MyD88 (25 ng), IRF-7 (25 ng), and full-length IRF-4 (0, 5, or 15 ng). Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after transfection. (f) The effect of IRF-4 on the nuclear translocation of IRF-5 induced by ODN1668 stimulation. RAW264.7 cells expressing YFP-IRF-5 alone or both YFP-IRF-5 and RFP-IRF-4 were placed on a time-lapse microscope, and images were obtained at 1-min intervals. Cells were stimulated or left unstimulated with 1 μM ODN1668 and incubated for up to 60 min in the presence of 10 ng/ml leptomycin B. The normalized YFP intensities of nuclear regions were plotted with time.