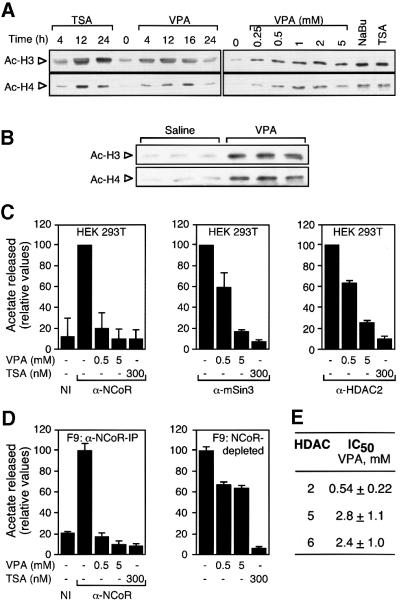
Fig. 3. VPA induces accumulation of hyperacetylated histone and inhibits HDAC activity. (A) HDAC inhibitors induce the accumulation of hyperacetylated histones H3 and H4. Both the time course and the required concentration for VPA-induced hyperacetylation were determined by western blot analysis of whole-cell extracts from F9 cells treated with VPA (1 mM if not indicated otherwise) in comparison with TSA (100 nM) and sodium butyrate (NaBu, 5 mM). Treatment was for 12 h or as indicated. Equal loading was confirmed by Coomassie Blue staining. Experiments were performed three times with similar results also in HeLa cells. (B) Histone hyperacetylation in vivo was determined by western blot analysis of histones H3 and H4 from mouse splenocyte nuclear extracts. Three mice each were injected i.p. with 25 ml/kg body weight of 155 mM solutions of NaCl or sodium valproate. Due to the short half-life of VPA in rodents, another dose (50%) was readministered after 5 h. Extracts were prepared 10 h after the initial dose. (C) HDAC activity was determined by the release of [3H]acetate from hyperacetylated radiolabeled histones. Activities were determined in the presence of the indicated compounds in immune precipitates from HEK293T cell extracts with antibodies directed against N-CoR, mSin3 or HDAC2. The HDAC activity which precipitated with a non-related immune serum (NI) was determined for control. Values are presented relative to the activity in the absence of HDAC inhibitors. The 100% values normalized for ∼1 mg of extract in representative experiments correspond to 1000 (N-CoR), 500 (mSin3) and 300 c.p.m. (HDAC2). Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments. (D) HDAC activity was determined in immune precipitates from F9 cell extracts with antibodies directed against N-CoR and in N-CoR-depleted extracts. Efficiency of N-CoR depletion was assessed by western blot for N-CoR in the IP pellet as well as in equivalent amounts of whole-cell extracts before and after depletion (data not shown). (E) IC50 values were calculated as those concentrations required for 50% inhibition of [3H]acetate release. HDAC assays were performed using immune precipitates from F9 cell extracts with antibodies directed against HDACs 2, 5 or 6. HDACs 5 or 6 were precipitated from extracts which had been depleted with antibodies directed against N-CoR, mSin3 and HDACs 1–3.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.