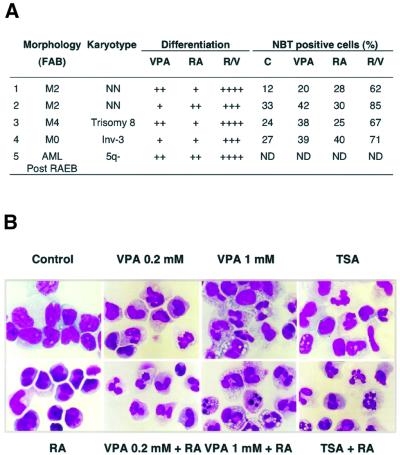
Fig. 8. VPA relieves the differentiation block in blast cells from AML patients. (A) Leukemic blasts of AML patients were cultured for 5 days in the absence or presence of RA and VPA (1 mM). Differentiation was evaluated by morphological criteria (+ 10–20%; ++ 20–40%; +++ 50–80%; ++++ 80–100% more mature metamyelocytes and granulocytes than control cultures) and by determination of the percentage of NBT-positive cells. Classification according to the French–American–British (FAB) nomenclature is given. Patients 1 and 2 represent newly diagnosed AML patients, whereas blasts of patients 3 and 4 were analyzed at relapse after chemotherapy. Patient 5 developed an AML after a refractory anemia with excess of blasts (RAEB). NN indicates a normal karyotype in leukemic blasts. ND, not determined. (B) Wright–Giemsa-stained primary blasts from the bone marrow of a newly diagnosed AML patient (patient 1 of A) were treated in culture for 5 days with RA (1 µM), VPA (0.2 or 1 mM), TSA (240 nM) as single agents or with a combination of RA and either VPA or TSA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.