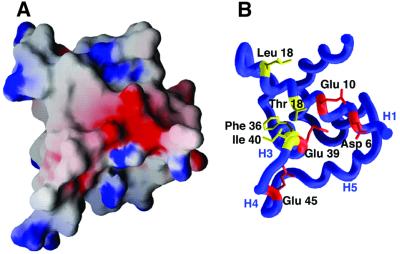
Fig. 7. Characteristics of the SR4-binding surface of AsiA. (A) Electrostatic potential map (drawn at ±9 kT) of the AsiA monomer viewed from the homodimer interface (Nicholls et al., 1991). Negatively charged surfaces are shown in red and positively charged surfaces in blue. (B) The negative patch seen in the center of the electrostatic surface is created by a collection of acidic residues (Asp6, Glu10, Glu39 and Glu45). These residues are hypothesized to be at least partially buried at the AsiA–SR4 interface. Hydrophobic amino acids which also make up part of the SR4 binding surface are shown in yellow.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.