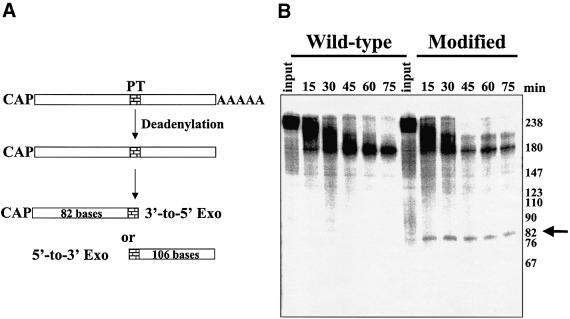
Fig. 2. Phosphothioate-modified RNAs demonstrate that RNAs are degraded by a 3′–5′ exonuclease following deadenylation. A synthetic RNA containing three consecutive phosphothioate substitutions was prepared and ligated to RNA fragments containing a 5′ cap and a 3′ poly(A) tail as described in Materials and methods. Polyadenylated wild-type or phosphothioate-modified variants of GemARE-A60 RNA were incubated in the in vitro deadenylation/decay system using HeLa cytoplasmic extracts for the times indicated. As shown in (A), trapping of an 82-base intermediate would identify a block by the phosphothioate modification to 3′–5′ exonucleases, while trapping a 106-base fragment would be consistent with decay via a 5′–3′ exonucleolytic pathway. (B) Reaction products were analyzed on a 5% acrylamide gel containing 7 M urea. The arrow on the right indicates the 82-base fragment that was trapped specifically by the phosphothioate modifications.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.