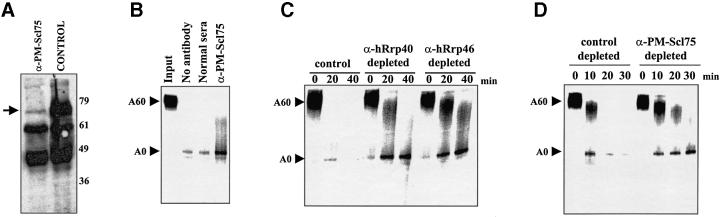
Fig. 4. The exosome is required for 3′–5′ exonucleolytic decay of the body of RNA substrates in in vitro deadenylation/decay assays. HeLa S100 cytoplasmic extracts were immunodepleted using anti-PM-Scl75 mouse antiserum or pre-immune serum prior to their use in in vitro RNA deadenylation/decay assays. (A) Western blotting with PM-Scl75 antiserum demonstrates that most of the endogenous PMScl-75 protein (indicated by the arrow) was removed by immunodepletion with anti-PM-Scl75 antiserum (lane α-PM-Scl75) but not by normal mouse serum (control lane) in the extracts used for the assay in (B). (B) Capped and polyadenylated GemARE-A60 RNA was incubated in the in vitro deadenylation/decay assay for 30 min using either untreated S100 extract (lane no antibody), extract that was treated with normal serum (lane normal sera) or extract that had been immunodepleted with antibodies specific for PM-Scl75 protein (lane α-PM-Scl75). Reaction products were analyzed on a 5% acrylamide gel containing 7 M urea. The positions of the polyadenylated input and deadenylated RNAs are indicated on the left. (C and D) Capped and polyadenylated GemARE-A60 RNA was incubated in the in vitro deadenylation/decay assay for the times indicated using either extract that was untreated (control lanes), extract that was treated with normal serum (control depleted lanes) or extract that had been immunodepleted with antibodies specific for PM-Scl75 protein (lanes α-PM-Scl75 depleted), hRrp40 protein (lanes α-hRrp40 depleted) or hRrp46 protein (lanes α-hRrp46 depleted). Reaction products were analyzed on a 5% acrylamide gel containing 7 M urea. The positions of the polyadenylated input and deadenylated RNAs are indicated on the left.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.