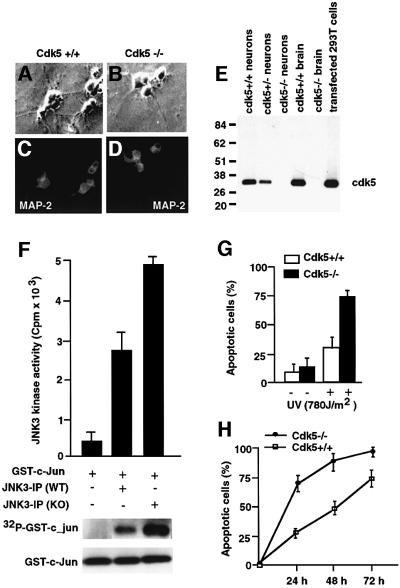
Fig. 7. Characterization of cortical neuronal culture from cdk5–/– and wild-type mice. (A–D) Immunocytochemical analysis of wild-type and cdk5–/– cortical neurons, showing expression of neuron-specific protein MAP-2 in all cultured cells. (E) Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates of wild-type, cdk5–/– and cdk5–/+ cultured cortical neurons. The positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are shown on the left. The position of cdk5 is indicated. (F) JNK3 was immunoprecipitated from wild-type and cdk5–/– cortical neurons using anti-JNK3 antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase reaction with GST–c-Jun as substrate in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. (G) Cdk5-deficient cells are more sensitive to apoptotic stimuli. Apoptotic cells are normalized. Apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining. Open bars correspond to wild type; solid bars correspond to cdk5–/– cells. The data are presented from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean expressed as a percentage. (H) Cdk5-deficient cells show increased sensitivity to apoptotic stimuli. The cells were treated as described in (G) and cell death was monitored for 3 days at different times after UV irradiation. Squares correspond to wild type and circles to cdk5–/–. The data are from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean expressed as a percentage.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.