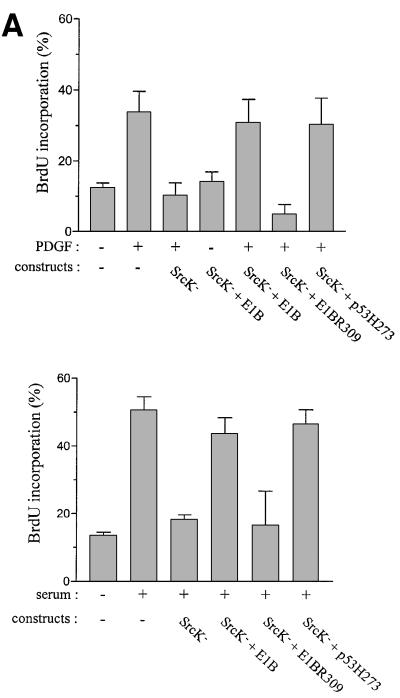
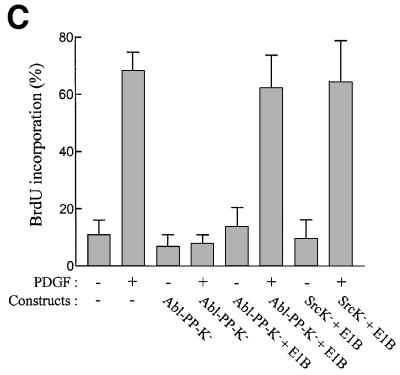
Fig. 3. Like SrcK–, Abl-PP-K– G1 block is overcome when inhibiting p53 function. (A) Inactivation of p53 rescues the G1 block induced by kinase-inactive Src (SrcK–) in MEF cells. Cells were plated onto coverslips and transiently co-transfected with SrcK– and the indicated construct. After serum starvation, cells were stimulated or not with PDGF (top panel) or serum (bottom panel) in the presence of BrdU for 18 h. (B) Inactivation of p53 rescues the G1 block induced by kinase-inactive Abl (Abl-PP-K–) in MEF cells. Cells were plated onto coverslips and transiently co-transfected with Abl-PP-K– and the indicated construct, and treated as in (A). (C) Inactivation of p53 rescues the PDGF mitogenic response inhibited by SrcK– or Abl-PP-K– in NIH 3T3 cells. Cells were plated onto coverslips and transiently transfected either with SrcK– or Abl-PP-K– in the presence or absence of E1B, then treated as in (A). Cells were fixed, stained for kinase expression and BrdU incorporation by double immunostaining, and analysed by microscopy. Shown is the percentage of BrdU-positive cells present in expressing and non-expressing cells under the specified conditions, as calculated in the legend to Figure 2. The data from three to five independent experiments have been averaged, and the mean and standard deviation are shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.