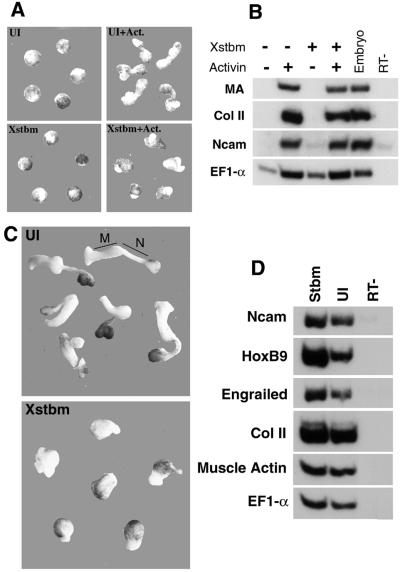
Fig. 4. Stbm blocks elongation of activin-induced animal caps and Keller sandwich explants. (A) Animal cap explants cultured in activin-containing medium extend during gastrula and neurula stages; this elongation is blocked by animal hemisphere injection of 0.5 ng of Xstbm. Explants are shown at stage 18. (B) RT–PCR from the same experiment demonstrates that markers of the cell populations that normally participate in convergent extension—notochord (collagen II), somitic mesoderm (muscle actin, MA) and neuroectoderm (Ncam)—are expressed at wild-type levels in Xstbm-injected caps. UI: uninjected caps. (C) Keller sandwiches were made from embryos injected with Xstbm RNA (0.5 ng) and from control embryos at early gastrula stages (see Materials and methods). After culture until sibling embryos reach the end of neurulation, control explants are highly elongated, and mesodermal (M) and neural (N) domains can be distinguished by pigmentation and morphology. Explants from Xstbm-injected embryos extend poorly and do not become clearly divided into mesodermal and neural domains. (D) Both mesodermal and neural markers are well expressed in Stbm-injected explants. Engrailed and HoxB9 are anterior and posterior neural markers, respectively.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.