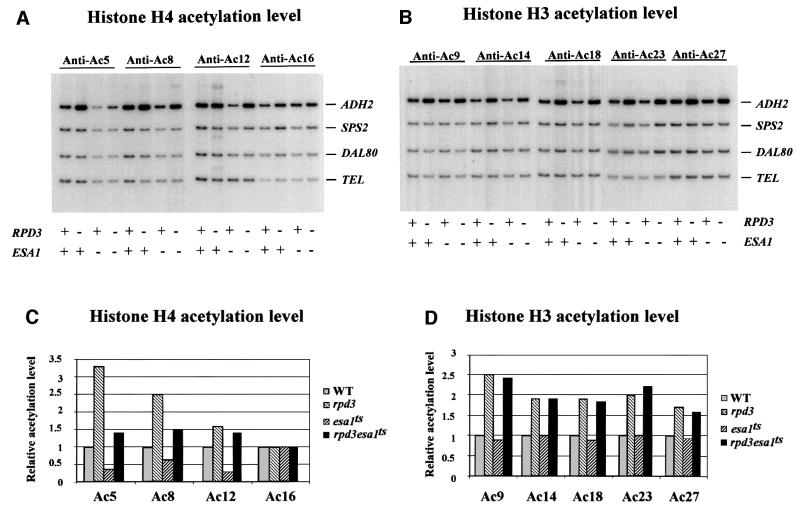
Fig. 2. Effects of histone acetyltransferase ESA1 on acetylation of histones at the ADH2 promoter. ChIP demonstrating the effects of histone acetyltranferase esa1ts mutant on the acetylation of (A) histone H4 sites K5, K8, K12 and K16, and (B) histone H3 sites K9, K14, K18, K23 and K27. The ADH2 fragment spans the region from –223 to +114, relative to the ATG. Amplification of a 138 bp fragment 0.5 kb from the telomere (Tel) of chromosome VI-R was used as a reference to ensure equal loading of samples. Yeast strains used for ChIP were WT (LPY3431), rpd3 (NSY164), esa1ts (LPY3430), rpd3/esa1ts (NSY165). SPS2 and DAL80 were found to be relatively unaffected by these mutations and were used as negative controls. (C and D) Quantification of the increase in H4, H3 acetylation in mutant cells relative to wild-type cells. [α-32P]dATP was added to the PCR mixture, and the PhosphorImager was used to quantitate the intensity of ADH2 PCR bands in these mutants relative to WT after normalizing to the TEL bands.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.