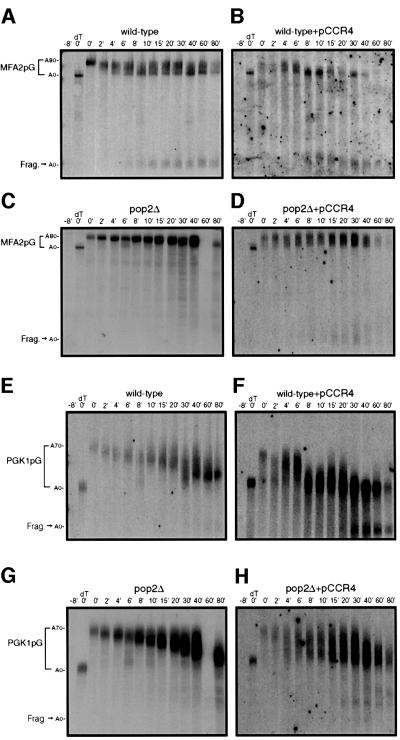
Fig. 2. Transcriptional pulse–chase analysis of the MFA2pG and PGK1pG transcripts. Shown are polyacrylamide northern gels examining the decay of MFA2pG (A–D) and PGK1pG (E–H) in wild-type, ccr4Δ and pop2Δ strains containing either a Flag-Ccr4p over-expression plasmid (pRP1045) or vector control as indicated. Numbers above the lanes are minutes after transcriptional repression by the addition of glucose following an 8 min induction of transcription (Decker and Parker, 1993). The 0 min time point was treated with RNase H and oligo(dT) to indicate the position of the deadenylated mRNA. Here, and in all subsequent figures, poly(A) tail lengths were determined by comparison of bands to size standards and the poly(A)– mRNA species generated by cleavage of RNase H and oligo(dT) (data not shown).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.