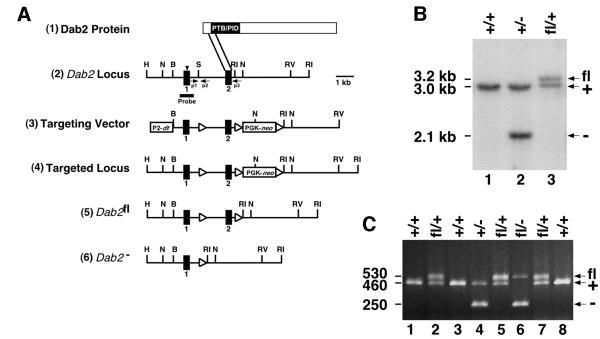
Fig. 1. Targeted disruption of the Dab2 gene. (A) Dab2 targeting strategy. (1) Schematic representation of the Dab2 protein. The parallel lines indicate the region of the Dab2 protein encoded by the second coding exon and targeted for deletion. (2) Partial restriction map of the Dab2 genomic locus in which the initiation ATG is indicated by the arrowhead. (3) Targeting vector containing the diphtheria toxin gene (dt) under the control of the RNA polymerase 2 promoter (P2) and the neomycin resistance gene (neo) under the control of the PGK promoter. LoxP sites are indicated by the triangles. (4) The targeted Dab2 locus prior to Cre expression. (5) The floxed Dab2 allele (Dab2fl) and (6) the deleted Dab2 allele (Dab2–) following Cre expression. Restriction enzymes: H, HpaI; N, NcoI; B, BamHI; S, SmaI; RI, EcoRI; RV, EcoRV. (B) Southern blotting analysis of DNA prepared from a wild-type mouse (lane 1), or mice heterozygous for either the deleted (lane 2) or floxed (lane 3) allele. DNA was digested with NcoI and hybridized to the radiolabeled Dab2 probe shown in (A). The positions of the wild-type (3.0 kb, +), null (2.1 kb, –) and floxed (3.2 kb, fl) alleles are indicated. (C) PCR analysis of P8 pups born from a Dab2fl/+ × Dab2+/– mating. The positions of the wild-type (460 bp, +), null (250 bp, –) and floxed (530 bp, fl) alleles are indicated. The positions of the three PCR primers used (p1, p2 and p3) are indicated by arrows in (A).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.