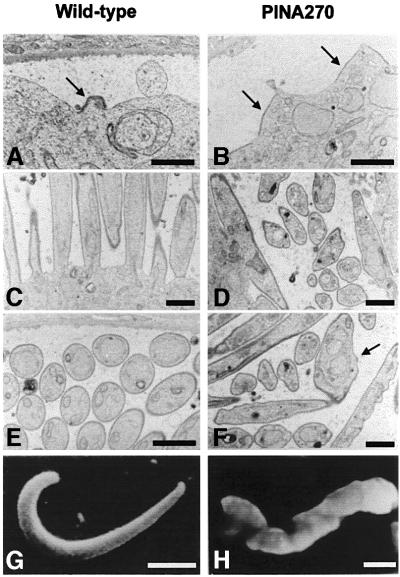
Fig. 8. Transmission electron micrographs showing sections of wild-type and PINA270 oocysts. (A) Focal emergence and extension of inner membranes (arrow) underneath the plasma membrane at a sporozoite bud site in a wild-type oocyst. Bar: 3 µm. (B) In PINA270 oocysts, inner membranes (arrows) delineate areas of the plasma membrane that are larger than in wild-type oocysts. Bar: 3 µm. (C) Sporozoite buds elongate perpendicular to the sporoblast periphery in wild-type oocysts. Bar: 1.5 µm. (D) In PINA270 oocysts, budding often occurs parallel to the sporoblast periphery. Bar: 1.5 µm. (E) Cross- sections of fully formed sporozoites, which are of homogenous sizes and shapes. Bar: 1.5 µm. (F) Longitudinal and cross-sections of sporozoites, which are of variable sizes and shapes. Note the presence of two nuclei surrounded by a single nuclear envelope in one of the sporozoites (arrow) and the ‘corrugated’ appearance of the sporozoite pellicles. Bar: 1.5 µm. (G and H) Scanning electron micrographs of free wild-type (G) and PINA270 (H) midgut sporozoites isolated from infected mosquitos at day 14 post-infection. Note the corrugated surface of the PINA270 sporozoite. Bars: 2 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.