Abstract
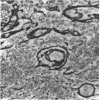
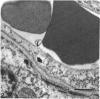
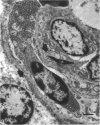
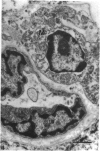
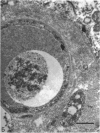
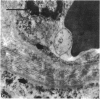
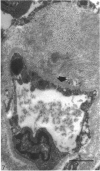
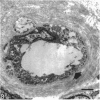
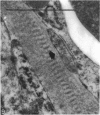
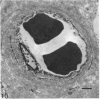
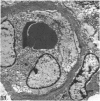
The deposition of collagen in the walls of capillary-size blood vessels was studied in 95 human thymuses with respect to the site of deposition, extent of the change and relation to age and degree of involution. When examined by electron microscopy the collagen was found to be situated between the 2 basement membranes of the so-called 'double-layered' capillaries characteristic of the thymus of many species. This results in the formation of substantial 'collars' of collagen around a proportion of the blood vessels examined. Few such collars are seen before birth, but their number and thickness increase markedly during the 1st year of life. The relationship of these changes to the degree of involution is less apparent. The significance of these changes to thymic structure and function is discussed in relation to cell traffic through the thymus and the postulated 'blood-thymus barrier', the existence of which is seen to be in some doubt.
Full text
PDF
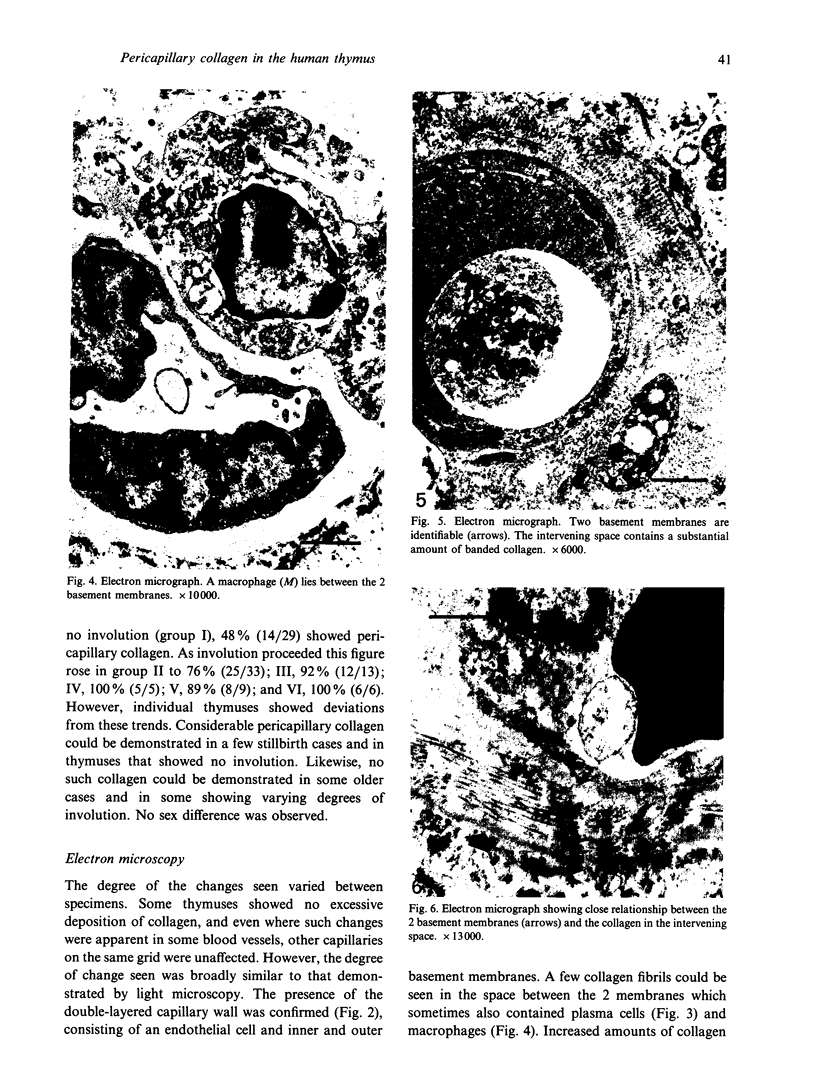
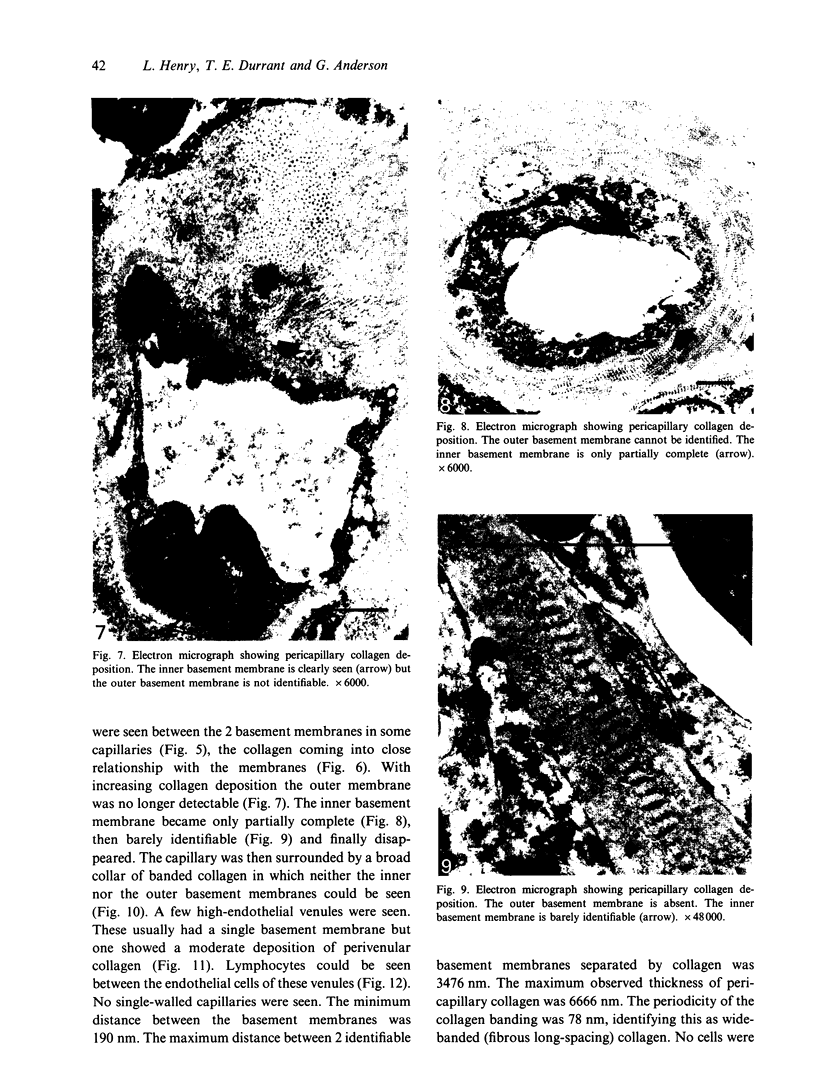
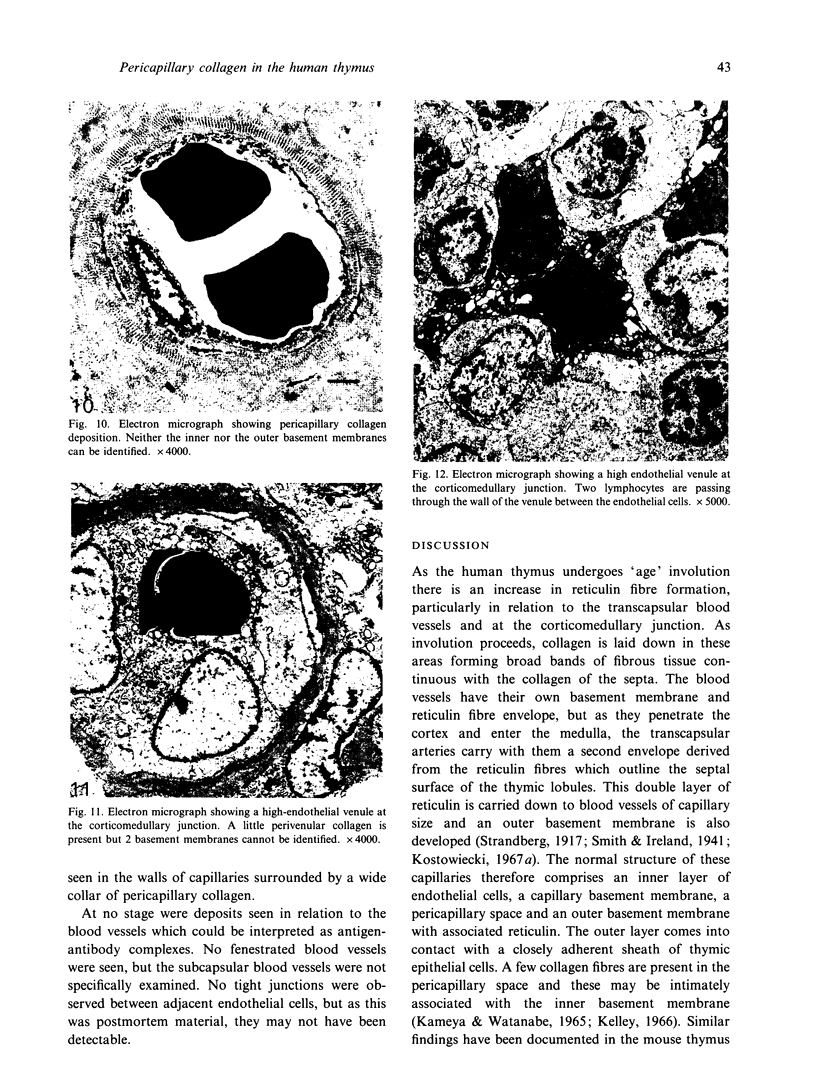



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Ito T. Vascular permeability in the thymus of the mouse. Arch Histol Jpn. 1974 Mar;36(4):251–264. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.36.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N., Mayrhofer G. Bone marrow origin of Ia-positive cells in the medulla rat thymus. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1666–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. IA antigens and antigen-presenting function of thymic macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1433–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N. Histological changes and macrophage activity in the adult guinea-pig thymus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Apr;52(2):142–146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N., Veall N. The uptake and localization of proteins, Evans Blue and carbon black in the normal and pathological thymus of the guinea-pig. Immunology. 1967 Apr;12(4):363–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant B. J., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Thymus lymphocytes. Efflux and restoration phases after peripheral exposure of mice to phytohaemagglutinin. Immunology. 1975 Jul;29(1):115–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant B. J. Renewal and fate in the mammalian thymus: mechanisms and inferences of thymocytokinetics. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):38–45. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK S. L., Jr The thymus in mice of strain 129/J, studied with the electron microscope. Am J Anat. 1963 Jan;112:1–33. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., Schutte R., Köhler Y. G., Korn C., Hoefsmit E. C. Characterization of the population of phagocytic cells in thymic cell suspensions. A morphological and cytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;231(2):313–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00222183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN I., BLOCH K. UPTAKE OF PARTICULATE MATTER WITHIN THE THYMUS OF ADULT AND NEW-BORN MICE. Nature. 1963 Dec 14;200:1099–1101. doi: 10.1038/2001099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galton M., Reed P. B. Entry of lymph node cells into the normal thymus. Transplantation. 1966 Mar;4(2):168–177. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196603000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugas J. M., Payne S., Wharton F. P. Association of macrophage lipids with Mycobacterium lepraemurium in the mouse thymus and lymph node. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Feb;51(1):87–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry L., Anderson G. Epithelial-cell architecture during involution of the human thymus. J Pathol. 1987 Jul;152(3):149–155. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry L., Anderson G. Immunoglobulin-producing cells in the human thymus. Thymus. 1988;12(2):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry L., Anderson G. Immunoglobulins in Hassall's corpuscles of the human thymus. J Anat. 1990 Feb;168:185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry L. Involution of the human thymus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):661–671. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess M. W., Mueller C., Schaffner T., Gerber H. A., Eggli P., Cottier H. Thymic lymphopoiesis: protected from, or influenced by, external stimulation? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;459:14–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb20811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino S., Takasugi N., Murakami T. Vascular architecture of thymus and lymph nodes, blood vessels, transmural passage of lymphocytes, and cell-interactions. Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;(Pt 3):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., Norton A. J., Addis B. J. The human thymus contains a novel population of B lymphocytes. Lancet. 1987 Dec 26;2(8574):1488–1491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92622-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Hoshino T. Light and electron microscopic observations on the vascular pattern of the thymus of the mouse. Arch Histol Jpn. 1966 Nov;27(1):351–361. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.27.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. E., COONS A. H., DEANE H. W. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; cellular distribution of pneumococcal polysaccharides types II and III in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):15-30, 4 pl. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTOWIECKI M. THE THYMIC MACROPHAGES. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1963;69:585–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameya T., Watanabe Y. Electron microscopic observations on human thymus and thymoma. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1965 May;15(2):223–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1965.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostowiecki M. Development of the so-called double-walled blood vessels of the thymus. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1967;77(3):406–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouvalainen K., Gitlin D. Passage of antigens across the vascular barrier of the thymus. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):592–593. doi: 10.1038/214592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramarsky B., Siegler R., Rich M. A. Presence of endothelial fenestrations in thymic capillaries of mice. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):464–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyewski B. A., Fathman C. G., Rouse R. V. Intrathymic presentation of circulating non-MHC antigens by medullary dendritic cells. An antigen-dependent microenvironment for T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):231–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kölsch E. Migration of macrophages carrying antigen into the thymus. Experientia. 1968 Sep 15;24(9):951–953. doi: 10.1007/BF02138677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckband E., Boyse E. A. Immunocompetent cells among mouse thymocytes: a minor population. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1258–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Allen P. M. Thymic cortical epithelial cells can present self-antigens in vivo. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):560–562. doi: 10.1038/337560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL A. H., WHITE R. G. The immunological reactivity of the thymus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Aug;42:379–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Holoshitz J., Eisenstein S., Reshef T., Rappaport S., Chemke J., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Effector T lymphocyte line cells migrate to the thymus and persist there. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):262–264. doi: 10.1038/300262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson I. A., Poste M. E. The vascular supply of the thymus in the guinea-pig and pig. Immunology. 1973 Feb;24(2):253–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. Blood capillaries of the heart and other organs. Circulation. 1961 Aug;24:368–388. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviola E., Karnovsky M. J. Evidence for a blood-thymus barrier using electron-opaque tracers. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):466–498. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAINTE-MARIE G. ANTIGEN PENETRATION INTO THE THYMUS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAINTE-MARIE G., LEBLOND C. P. Origin and fate of cells in the medulla of rat thymus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):909–915. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stet R. J., Wagenaar-Hilbers J. P., Nieuwenhuis P. Thymus localization of monoclonal antibodies circumventing the blood-thymus barrier. Scand J Immunol. 1987 May;25(5):441–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törö I., Oláh L. Studies on the blood--thymus barrier. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1967;18(2):135–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS L. Electron microscopic, observations on the vascular barrier in the cortex of the thymus of the mouse. Anat Rec. 1963 Mar;145:413–437. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091450306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]