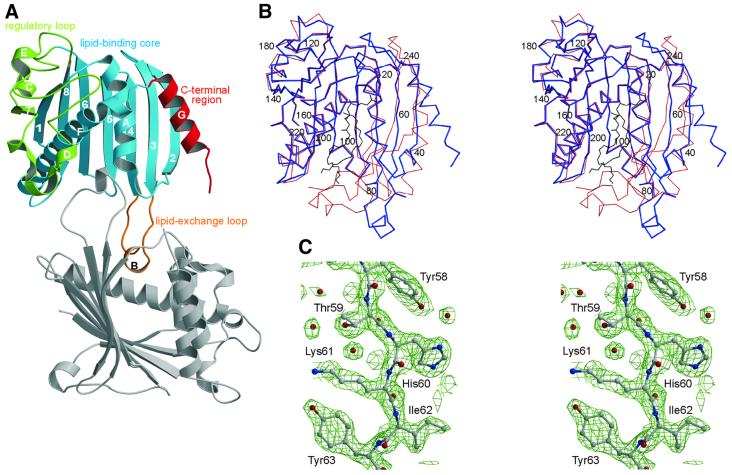
Fig. 1. Crystal structure of apo-PITPα revealing an open conformation stabilized through dimerization. (A) With functional regions color-coded: regulatory loop (green), lipid-binding core (blue), C-terminal region (red) and the lipid exchange loop (orange); secondary structural elements are labeled numerically (β-strands) and with upper case roman letters (α-helices). The lipid-binding site, located in the core of the molecule, is partially occupied by the lipid exchange loop of the symmetry-related, dimeric partner molecule (gray). (B) Stereo representation of the Cα trace of the open (blue) and closed, PC-encapsulated (red) conformations showing the major structural rearrangements of the lipid exchange loop, the C-terminal region and β-strands 2, 3 and 4; the position of every 20th residue is indicated. The position of PC in the PC-encapsulated form is shown in black. (C) Stereo view of the 2Fo – Fc electron density map contoured at 1.5σ of residues 58–63 of β-strand 3 preceding the lipid exchange loop.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.