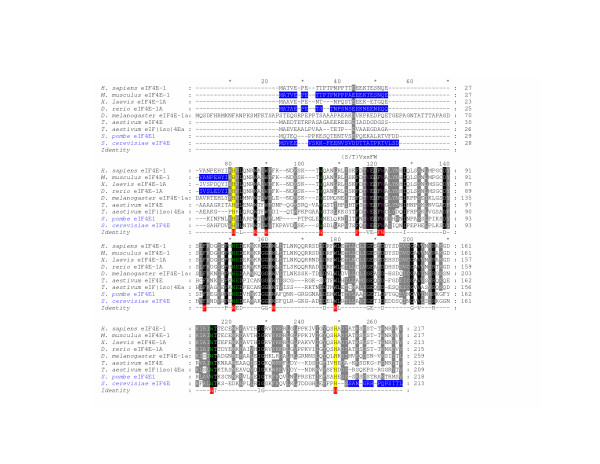
Figure 1.
An alignment of the amino acid sequences of selected established eIF4E-family members. An alignment of the complete amino acid sequences of H. sapiens eIF4E-1, M. musculus eIF4E-1, X. laevis eIF4E-1A, D. rerio eIF4E-1A, D. melanogaster eIF4E-1a, T. aestivum eIF4E and eIF(iso)4E, S. pombe eIF4E1, and S. cerevisiae eIF4E. eIF4E-family members with names in blue indicate that the sequence was estimated or verified using genomic sequence data. A sequence of identity is shown with aromatic residues boxed in red. Black and grey shading: conserved amino acids identical in all or similar in greater than 75 % of the sequences shown, respectively. Yellow shading: His-residues that border the conserved core region of an eIF4E-family member. Blue shading: regions of the respective eIF4E-family member that have been shown to be dispensable for eIF4E-function in vitro. Residues in green: positions of residues equivalent to Trp-56, Trp-102, Glu-103 and Trp-166 of H. sapiens and M. musculus eIF4E-1 that directly interact with the cap-structure. Residues in purple: identity with respect to residues Val-69 and Trp-73 of M. musculus eIF4E-1 that interact with eIF4G and 4E-BPs and are found within a region of eIF4E-family members possessing the concensus (S/T)VxxFW (as indicated). Numbers to the right of the sequences indicate the positions of residues from the N-terminal Met.