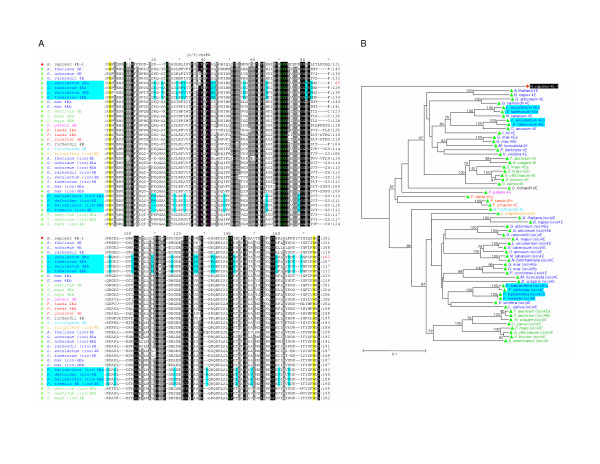
Figure 4.
Comparison of the conserved core regions of selected Class I eIF4E-family members from Viridiplantae. A. An alignment of the amino acid sequences representing the 'core' regions of Class I eIF4E-family members from the indicated species of Viridiplantae and of eIF4E-1 from H. sapiens. Amino acid residues within the alignment are highlighted as described in the legend to Figure 3A with the exception that residues shaded in grey indicate similar amino acids in more than 90% of the sequences shown. Numbers to the right of the alignment represent distances of amino acids with respect to the N-terminal Met residue (black) or, for eIF4E-family members for which the N-terminal Met could not be predicted, from the first residue shown (red). B. A phylogram constructed by neighbor-joining derived from alignments of nucleotide sequences representing the core regions of the indicated Class I-family members. Bootstrap values greater than 70% derived from 50,000 tests are shown to indicate supported nodes. For A and B: names of eIF4E-family members are highlighted to indicate taxonomic divisions: Eudicotyledons (blue), Liliopsida (green), Bryopsida (purple), Coniferopsida (red), Stem Magnoliophyta (cyan), Magnoliids (orange), Chlorophyceae (black), Mammalia (white on black). Names of family members and residues shaded in cyan indicate evidence that a gene-duplication occurred prior to speciation.