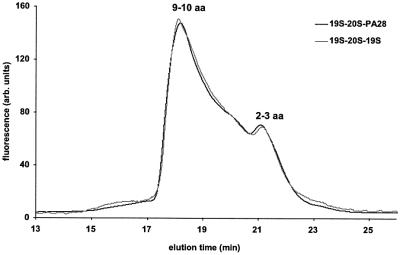
Fig. 7. Size distribution of peptides generated from IGF-1 by 26S and hybrid complexes. Peptides generated during degradation of IGF-1 were separated from undigested protein on a C18 Vydac column as described (Kisselev et al., 1998), and lyophilized. After lyophilization, the resuspended material was used for size-exclusion chromatography with a polyhydroxy-ethyl aspartamide column (0.46 × 20 cm, Poly LC, Columbia, MD), equilibrated with 0.2 M sodium sulfate, 25% acetonitrile pH 3.0 using an HP1090 chromatographer (Hewlett-Packard) and a fluorometer detector. Peptide products were resuspended in 0.1 M HEPES buffer pH 6.8. For each analysis, 3 nmol of peptides in a total volume of 20 µl were added to 10 µl of fluorescamine (0.3 mg/ml acetone). The reaction was terminated after 1 min with 30 µl of H2O and the sample was injected immediately into the HPLC column. To determine the apparent molecular mass of the peptides eluted, the column was calibrated each time before use with 11 standard amino acids and peptides in the 200–3500 Da range that had been derivatized with fluorescamine in the same way as proteasome products. Prior control studies showed that retention times of these fluorescamine-derivatized peptides were highly reproducible, and linearly dependent on the logarithm of their molecular weights (Kohler et al., 2001).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.