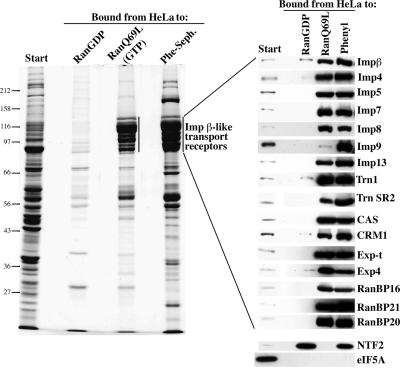
Fig. 1. Surface hydrophobicity is one marker for translocation competence. A cytosolic extract from HeLa cells was prepared and subjected to binding to immobilized RanGDP, RanGTP or phenyl-Sepharose (low substitution). Analysis of starting material and bound fractions was by SDS–PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining (left panel) or western blotting with antibodies raised against the indicated nuclear transport receptors (right panels). Phenyl-Sepharose retrieved Impβ transport receptors with specificity similar to that of RanGTP. Certain receptors (e.g. Imp9) were recovered with even higher efficiency by phenyl-Sepharose than by RanGTP. Likewise, NTF2 bound phenyl-Sepharose as efficiently as its import substrate RanGDP. In contrast, typical cytosolic proteins, such as eIF-5A, did not bind to the hydrophobic matrix under these stringent conditions (see also Materials and methods and main text). Load in the bound fraction corresponds to 20× the starting material.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.