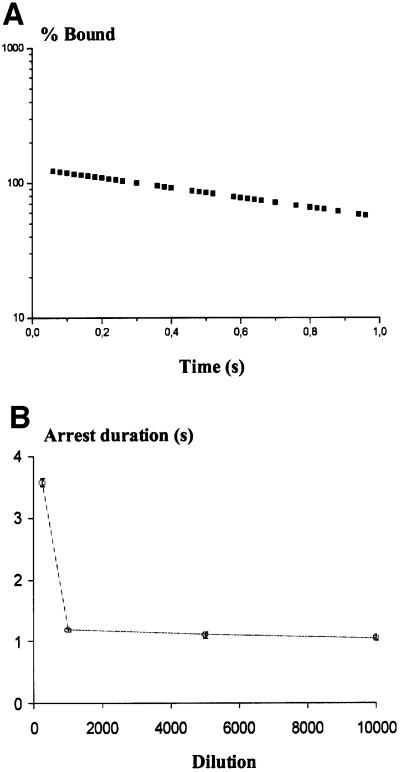
Fig. 8. Dissociation kinetics and dependence of dissociation rate on site density. (A) The motion of E/EC1–2-coated spheres along E/EC1–2-coated surfaces, and the duration of binding events were recorded. The number of bound particles was plotted against time after the initial stop. As shown for a representative example, the curve was linear on the time interval (0–1 s), consistent with first-order dissociation kinetics. (B) Mica surfaces were coated with various dilutions of an E/EC1–2 coating solution and used for dynamic study of interaction with E/EC1–2-coated spheres (wall shear rate 8/s). Each data point corresponds to 100–150 trajectory measurements; error bars are within the size of data points. At high protein density on mica (dilution 1/250), long arrest durations were observed (>3 s) corresponding to multiple binding interactions. At dilutions of 1/1000 (a site density of 50–100 E/EC1–2 molecules/µm2) or more, the dissociation rate was constant, indicating measurements of interactions between single E/EC1–2 fragments for binding site densities of 50–100 to 5–10 molecules/µm2.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.