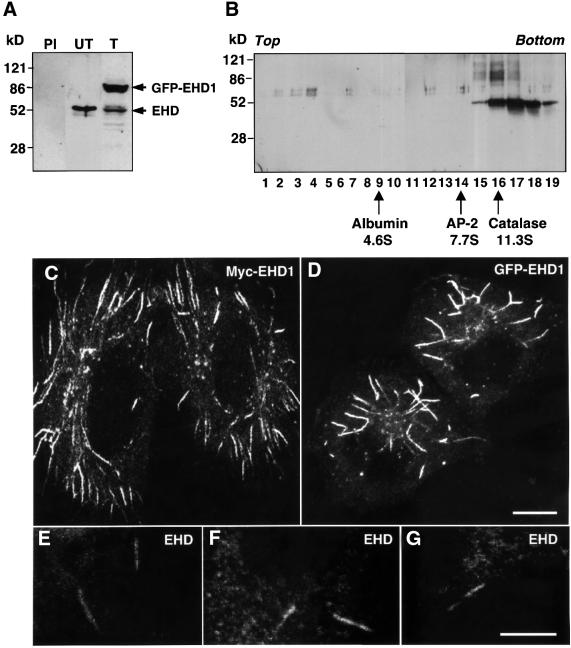
Fig. 2. EHD1 localizes to an array of long tubular structures. (A) Detergent lysates were prepared from untransfected HeLa cells (PI and UT) or HeLa cells transfected with a GFP–EHD1 construct (T), and resolved by 4–20% SDS–PAGE. Immunoblot analysis with either pre-immune serum (PI) or rabbit polyclonal antibody directed against EHD1 (UT and T) revealed the presence of both endogenous EHD1 (55 kDa) and transgenic GFP–EHD1 (85 kDa) proteins. Following transient transfection, ∼60% of the cells expressed detectable levels of EHD1, and the relative levels of transfected and endogenous proteins were estimated by densitometric analysis of multiple film exposures. (B) HeLa cell extracts were subjected to sedimentation velocity analysis on a 4–20% sucrose gradient. Fractions were collected, resolved by 4–20% SDS–PAGE, and proteins were visualized by immunoblot analysis using the polyclonal antibody prepared against EHD1. Size markers indicate the positions of albumin, AP-2 complex and catalase on the sucrose gradients. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding Myc-EHD1. Cells were fixed and permeabilized 24 h later, and incubated with a mouse monoclonal antibody to the Myc epitope. Bound antibodies were revealed by incubation with Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG, demonstrating the presence of a dense network of Myc-EHD1 tubular organelles. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding GFP–EHD1, and were fixed and permeabilized after 24 h. (E–G) Untransfected HeLa cells were fixed, permeabilized and incubated with a rabbit polyclonal antibody to endogenous EHD1. Bound antibodies were revealed by incubation with Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG. Images show the presence of long, tubular structures containing endogenous EHD proteins. All images were obtained by confocal microscopy. Bars: (C and D), 10 µm; (E–G), 10 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.