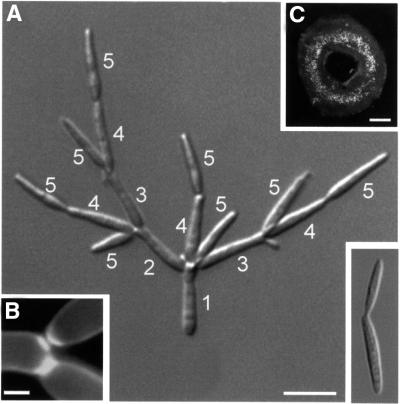
Fig. 7. Morphology and colony phenotype of a Δkin3 mutant strain. (A) In contrast to wild-type cells (small image at bottom right), the Δkin3 strain forms tree-like aggregates in liquid culture. This phenotype is most likely due to a cell separation defect in combination with a mono-polar budding pattern. The order of bud formation is indicated by white numbers. Bar: 10 µm. (B) Calcofluor staining showed that septa are formed, indicating that deletion of kin3 affects late steps of cell separation. Bar: 2 µm. (C) Morphology of RWS18 leads to ring-like colonies on agar plates. Bar: 0.4 mm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.