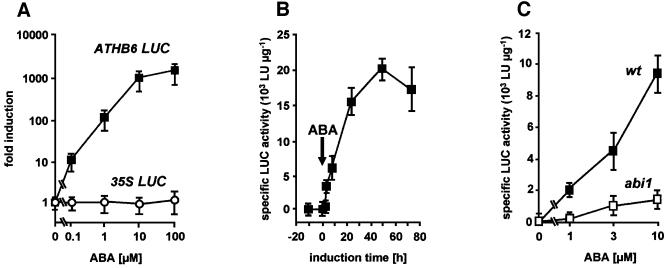
Fig. 5. ABA- and ABI1-dependent activation of the ATHB6 promoter. The regulation of the ATHB6 promoter was analysed by stable integration of an ATHB6 promoter driving LUC expression in Arabidopsis. (A) The specific LUC activity of seedlings homozygous for the ATHB6 reporter construct and the 35S LUC control was determined from extracts 24 h after ABA administration, respectively. Values are expressed as fold induction of specific LUC activity relative to the untreated control. (B) The time-dependent increase of specific LUC activity in the transgenic reporter line by 10 µM ABA. The arrow signifies the time point of challenge to exogenous ABA. (C) The ABI1 dependence of the ABA-mediated reporter activation was studied 24 h after ABA addition in bulked F2 seedlings from crosses of the reporter line to the ABA-insensitive abi1 mutant (abi1) and to the wild-type (wt) of the same ecotype to avoid ecotype-specific differences in ABA sensitivity. The Mendelian segregation of the dominant mutant trait results in a quarter of the seedlings of the F2 population expressing LUC in a wt ABI1 background. Specific activity is expressed as light units (LU) per µg of protein. The standard deviation among four independent experiments is indicated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.