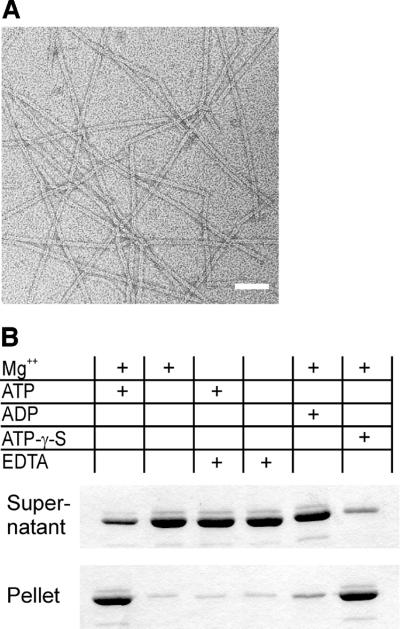
Fig. 3. (A) ParM polymers visualized by electron microscopy. Typical ParM filaments formed by incubation in 30 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT and 2 mM ATP-γ-S. Filament formation required Mg2+ and occurred in the presence of ATP or its non-hydrolysable analogue, ATP-γ-S, but not in the presence of ADP. Polymers have a cross-sectional diameter of ∼7 nm. Scale bar: 50 nm. (B) Nucleotide-dependent polmerization of ParM. Polymerization of 10 µM ParM was assayed in 30 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl and 1 mM DTT. MgCl2 (2 mM), EDTA (10 mM) and nucleotides (2 mM) were added as indicated. The protein was centrifuged immediately after mixing at 100 000 g for 15 min at ambient temperature. Supernatant and solubilized pellets were analysed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.