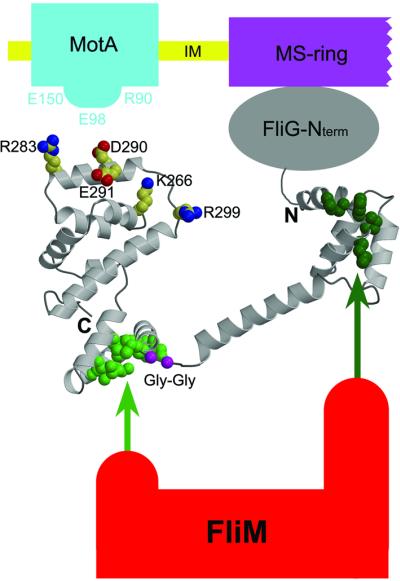
Fig. 6. Proposed arrangement of FliG-MC relative to other proteins of the flagellum. The charge-bearing ridge on the C-terminal domain is oriented to allow interactions with conserved charged residues of MotA. FliM binds to both domains of FliG-MC, most likely through the EHPQ motif in domain I (dark green) and the surface hydrophobic patch on domain II (light green). (FliM–FliG binding interactions are indicated by the arrows.) The flexible Gly–Gly linker (magenta) allows relative movement of the domains. We propose that CW/CCW switching occurs by movement of the C-terminal domain of FliG relative to the rest of the protein, under the control of FliM (see the text).
