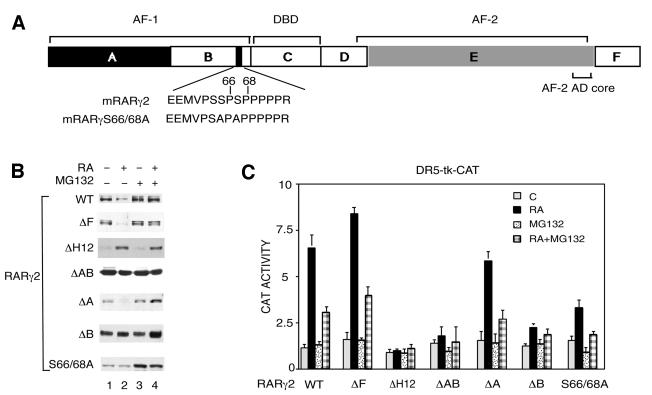
Fig. 3. Both the AF-1 and AF-2 activation domains contribute to the RA-induced degradation of RARγ2. (A) Schematic representation (not to scale) of mRARγ2 with the DBD and the functional AF-1 and AF-2 domains, which lie in the A/B and E regions, respectively. The target sequence for phosphorylation by proline-directed kinases in the B region is shown and the corresponding serine residues, which have been mutated to alanine (S66 and S68), are indicated. (B) COS-1 cells were cotransfected with the DR5-tk-CAT reporter construct and the expression vector for mRARγ2 either WT, ΔF, ΔH12, ΔAB, ΔA, ΔB or S66/68A and treated with vehicle or 1 × 10–6 M RA as indicated. When mentioned, MG132 was added 15 h before harvesting. Equal amounts of WCEs, as estimated by immunoblotting with actin antibodies (data not shown) were resolved by SDS–10% PAGE and immunoblotted with RPγ(F) or Ab5γ(D) in the case of RARγ2ΔF. (C) Cells transfected as in (B) were analyzed for CAT activity. The results are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.