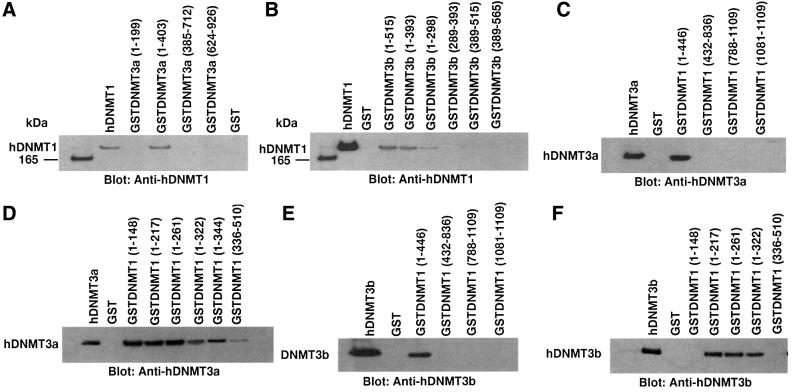
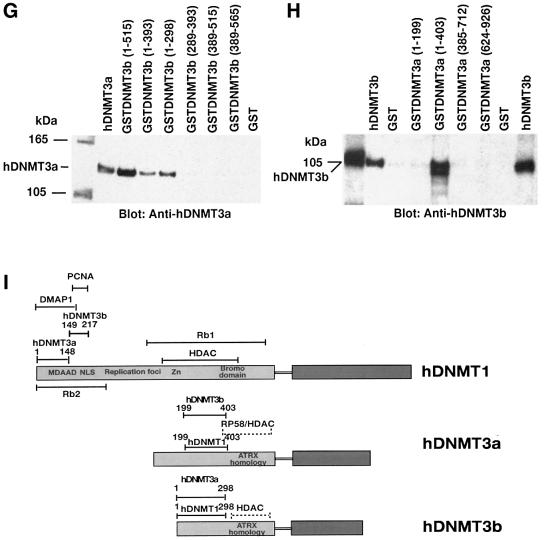
Fig. 3. Detailed mapping of the interacting regions of DNMTs. The GST–DNMT fusion peptides used for complex formation are indicated above each blot, with amino acid residue numbers shown in parentheses. Positive and negative controls are purified hDNMT1, hDNMT3a, hDNMT3b and GST protein, respectively. Molecular weight markers are in kDa. Antibodies used for the blots are indicated below each panel. (A) Immunoblot of bound hDNMT1 to various GST fusion fragments of hDNMT3a. (B) A similar immunoblot to that of (A) showing various GST fusion peptides of hDNMT3b bound to hDNMT1. (C) Identification of the hDNMT3a binding region of hDNMT1. (D) Finer mapping of the hDNMT1 binding region of hDNMT3a. (E) Immunoblot of bound hDNMT3b to various GST fusion fragments of hDNMT1. (F) Finer mapping of the hDNMT1 binding region of hDNMT3b. (G) hDNMT3a binding region of hDNMT3b. (H) hDNMT3b binding region of hDNMT3a. (I) Summary diagram of the various functional regions of DNMTs. Amino acid residues are indicated for various DNMTs. The relative locations of binding domains for other proteins are also indicated for reference. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), retinoblastoma gene product (Rb1), histone deacetylase (HDAC), DNA methyltransferase associated protein (DMAP) and methylated DNA-dependent allosteric activation domain (MDDAAD) are indicated. Another Rb binding region (Rb2) was recently discovered and mapped at the N-terminus of hDNMT1. Amino acid residues for protein–protein interaction are indicated for all hDNMTs.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.