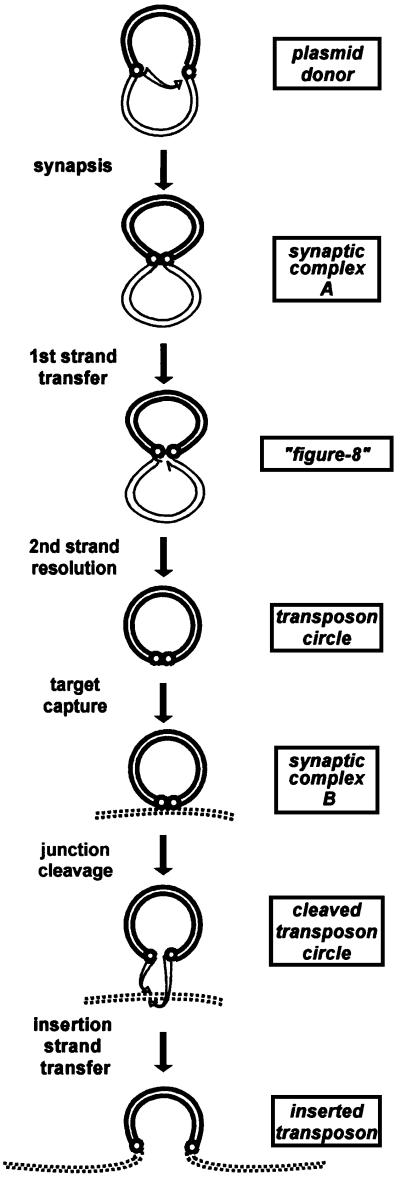
Fig. 1. Proposed IS911 transposition pathway. Transposon DNA (bold lines), donor backbone sequences (fine lines), target DNA (dotted lines), IRL and IRR (small circles). The different steps of IS911 transposition are shown: synapsis of the ends in a plasmid donor to generate synaptic complex A; strand cleavage at one end (the donor end) and transfer to the other (the target end) to form a figure-of-eight structure in a reaction that requires only the transposase OrfAB; second strand resolution requiring host functions but no IS911 proteins to generate the transposon circle; synapsis with a target DNA molecule (synaptic complex B); cleavage of the IRR–IRL junction; and transfer into the target, which requires the transposase OrfAB. Final insertion requires OrfAB and is greatly stimulated by OrfA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.