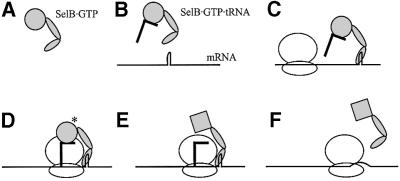
Fig. 8. Proposed model for SelB function in stop codon read through. (A) SelB binds GTP. (B) SelB·GTP binds Sec-tRNASec. (C) SelB·GTP·Sec-tRNASec binds to an mRNA hairpin in a selenoprotein gene. Upon binding, SelB-C undergoes a conformational change so that the L is opened. SelB is ready to deliver Sec-tRNASec to the A-site of the approaching translating ribosome. (D) When the UGA codon is available in the A-site, SelB-N swings in the tRNA. If a correct codon–anticodon match occurs, GTP is hydrolysed. (E) SelB changes conformation to the GDP form and releases the tRNA that is accommodated in the peptidyl-transfer site. (F) SelB leaves the mRNA hairpin, perhaps simultaneously with the combined unwinding and translocation of mRNA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.