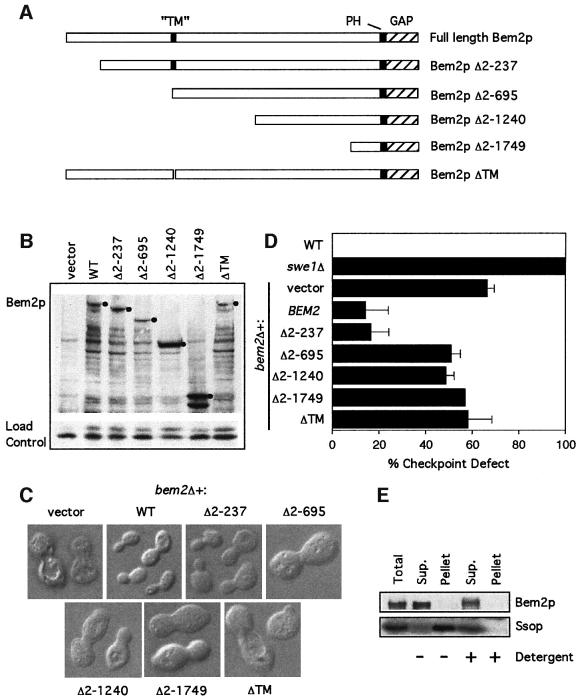
Fig. 5. Deletion anaylsis of the N-terminal domain of Bem2p. (A) Domain structure of Bem2p, showing the C-terminal GAP domain, the PH domain and the putative transmembrane (TM) domain. Also illustrated are the regions of the protein missing in the various deletion constructs. (B) The bem2Δ strain DLY4015 containing the plasmids pRS316 (vector), pDLB768 (WT), pDLB2147 (Δ2–237), pDLB2118 (Δ2–695), pDLB2116 (Δ2–1240), pDLB2115 (Δ2–1749) or pDLB2249 (ΔTM) was grown to exponential phase in dextrose-containing media. Cell lysates from these strains were immunoblotted with an anti-myc antibody. The bands corresponding to full-length protein for each construct are marked with a filled circle. (C) Images of live cells from the same strains were captured using DIC microscopy. (D) The indicated strains were assayed for checkpoint function as in Figure 2A. (E) Cells of strain DLY4860 (BEM2-myc) were lysed and fractionated by ultracentrifugation at 250 000 g for 1 h. Pellet fractions were resuspended to the same volume as the supernatant and equal volumes were analyzed by immunoblotting with α-myc and α-Sso1/2p antibodies.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.