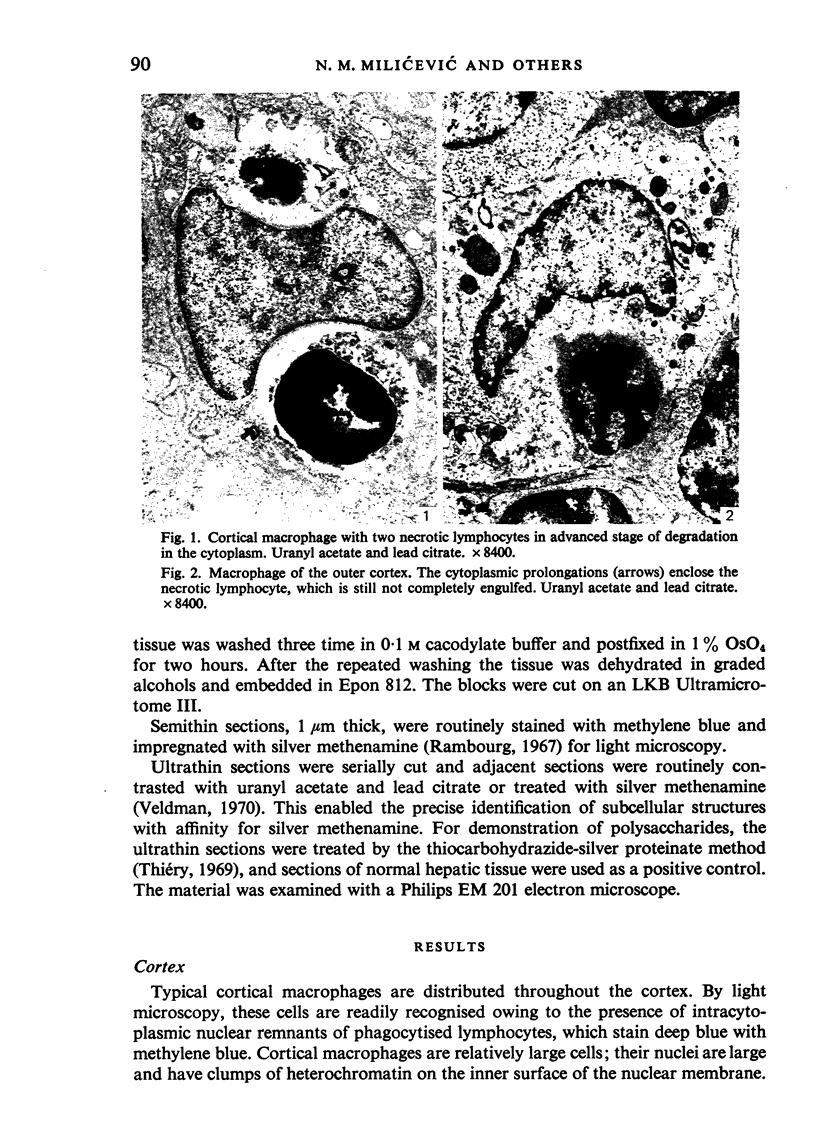
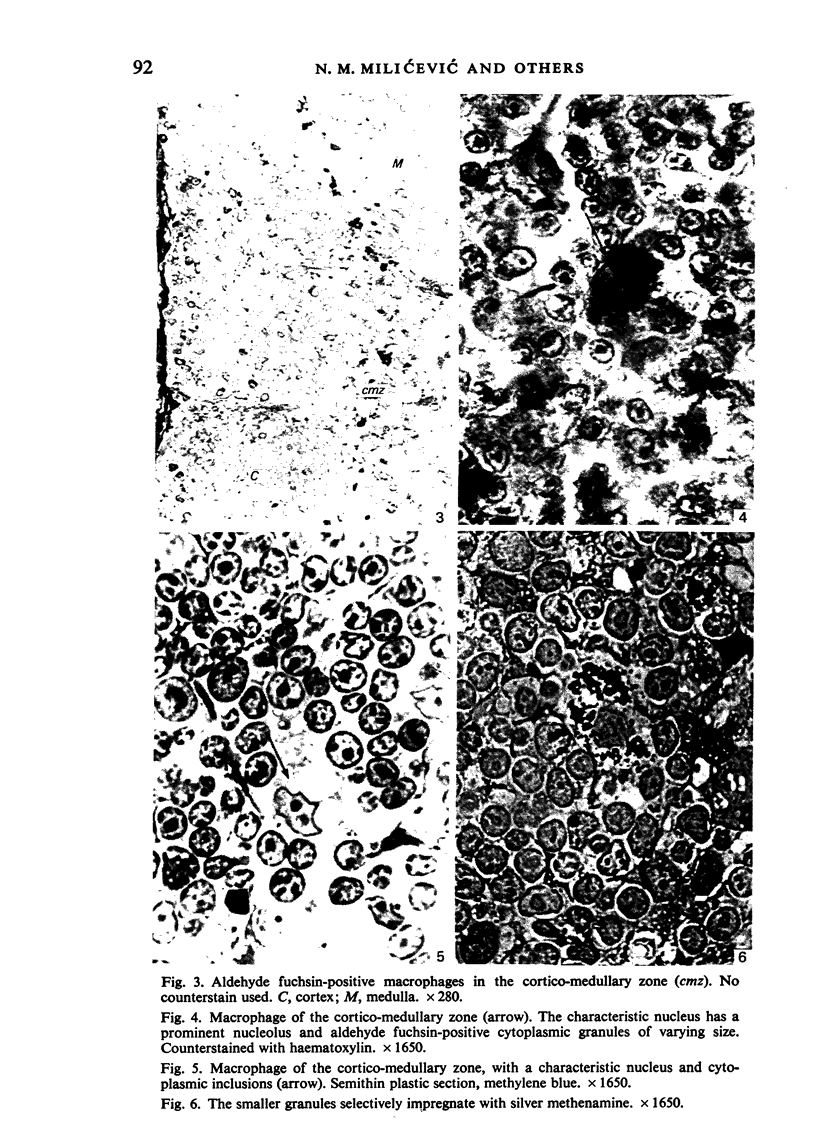
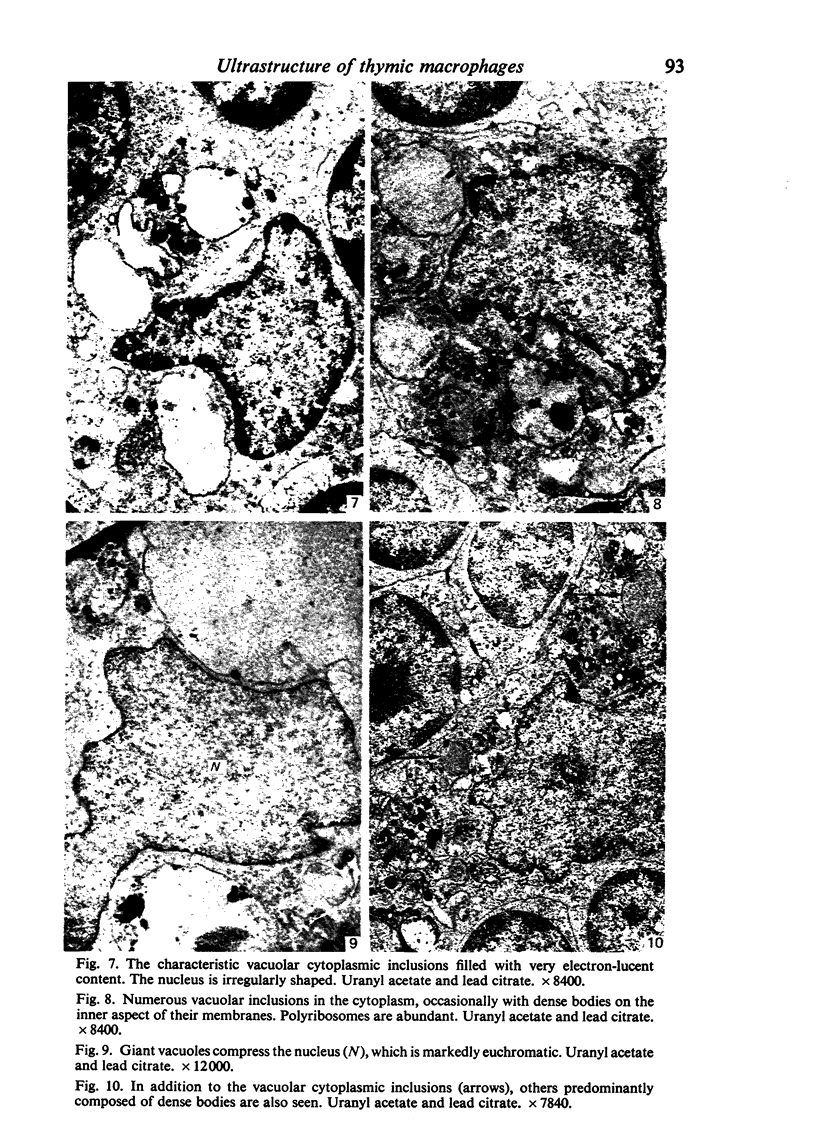
Abstract
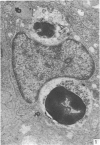
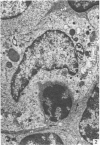
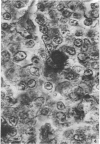
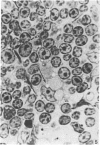
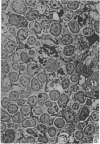
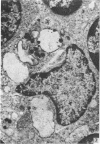
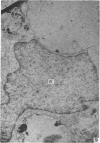
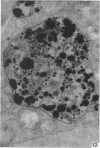
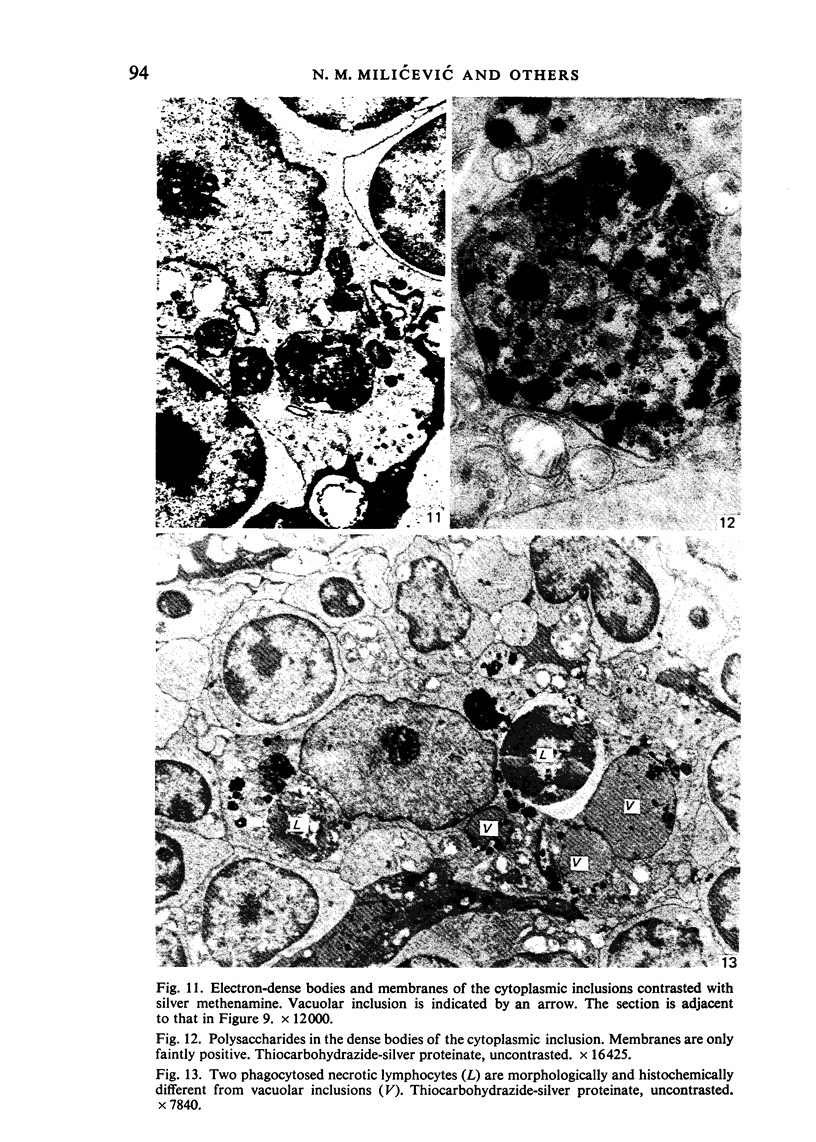
Electron microscopic study of the normal rat thymus has demonstrated that macrophages with different ultrastructural features are positioned in the thymic cortex, in the cortico-medullary zone and in the medulla. Phagocytic cells, containing necrotic lymphocytes in various stages of degradation, are distributed throughout the thymic cortex. The cortico-medullary zone, in contrast, is populated with macrophages displaying specific ultrastructural features. These cells contain numerous vacuolar inclusions of different size, filled with homogeneous, flocculent material of very low electron density. The dense bodies, occasionally positioned to the inner side of the vacuolar membrane, selectively contrast with silver methenamine and contain polysaccharides, as demonstrated by the thiocarbohydrazide-silver proteinate method. Very rarely, these cells contain phagocytosed lymphocyte remnants. The predominant type of mononuclear phagocytic cells in the thymic medulla are the interdigitating cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel H. Ultrastructure of the involuting thymus in mice. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1979;93(3):537–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearman R. M., Levine G. D., Bensch K. G. The ultrastructure of the normal human thymus: a study of 36 cases. Anat Rec. 1978 Mar;190(3):755–781. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Thymic macrophages modulate one stage of T cell differentiation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1861–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brelińska R., Kaczmarek E., Warchoł J. B., Jaroszewski J. Distribution of different cell types within the rat thymus in the neonatal period of life. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;240(2):473–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00222362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brune K., Glatt M., Kälin H., Peskar B. A. Pharmacological control of prostaglandin and thromboxane release from macrophages. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):261–263. doi: 10.1038/274261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK S. L., Jr The thymus in mice of strain 129/J, studied with the electron microscope. Am J Anat. 1963 Jan;112:1–33. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., Hoefsmit E. C. Ultrastructure of the rat thymus: the micro-environment of T-lymphocyte maturation. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;218(2):279–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00210344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., Köhler Y. G., Hoefsmit E. C. Interdigitating cells and macrophages in the acute involuting rat thymus. An electron-microscopic study on phagocytic activity and population development. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(2):291–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00216874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., Sminia T., Kohler Y. G., Janse E. M., Hoefsmit E. C. Rat thymus micro-environment: an ultrastructural and functional characterization. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;149:441–446. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-9066-4_61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Savion N. Cultivation, proliferation and characterization of thymic macrophages. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):139–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Abbot A., Mackay I. R. An electron-microscope study of the human thymus: normal appearances and findings in myasthenia gravis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):211–215. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSHINO T. Electron microscopic studies of the epithelial reticular cells of the mouse thymus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;59:513–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00368725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haar J. L. Light and electron microscopy of the human fetal thymus. Anat Rec. 1974 Aug;179(4):463–476. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091790406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang W. S., Ho T. Y., Luk S. C., Simon G. T. Ultrastructure of the rat thymus. A transmission, scanning electron microscope, and morphometric study. Lab Invest. 1974 Nov;31(5):473–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Hoshino T. Fine structure of the epithelial reticular cells of the medulla of the thymus in the golden hamster. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;69:311–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00406283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug H., Mager B. Ultrastructure and function of interdigitating cells in the guinea pig thymus. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung. 1979;27(1-2):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDING B. H., HALL H. E., WEST C. D. Aldehyde-fuchsin-positive material of the posterior pituitary; its nature and significance. Lab Invest. 1956 May-Jun;5(3):256–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T. Ultrastructure of epithelial cells in the cortex of guinea pig thymus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;92(2):159–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00335644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milićević N. M., Milićević Z., Piletić O., Mujović S., Ninkov V. Reactivity of thymic metallophilic cells during the regeneration after the application of cyclophosphamide. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Dec;34(6):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Poulter L. W., Turk J. L. Effect of lymphocyte mediators on macrophages in vitro. A correlation of morphological and cytochemical changes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Mar;13(3):455–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiernik M., Homo-Delarche F. Thymic reticulum in mice. III. Phagocytic cells of the thymic reticulum in culture secrete both prostaglandin E2 and interleukin 1 which regulate thymocyte proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):689–692. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D. Ultrastructure of human fetal thymus. Am J Dis Child. 1968 Feb;115(2):222–238. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1968.02100010224012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Turk J. L. Studies on the effect of soluble lymphocyte products (lymphokines) on macrophage physiology. II. Cytochemical changes associated with activation. Cell Immunol. 1975 Nov;20(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A. An improved silver methenamine technique for the detection of periodic acid-reactive complex carbohydrates with the electron microscope. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Jul;15(7):409–412. doi: 10.1177/15.7.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streefkerk J. G., Veerman A. J. Histochemistry and electron microscopy of follicle lining reticular cells in the rat spleen. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;115(4):524–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00335718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haelst U. Light and electron microscopic study of the normal and pathological thymus of the rat. I. The normal thymus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;77(4):534–553. doi: 10.1007/BF00319347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wijngaert F. P., Kendall M. D., Schuurman H. J., Rademakers L. H., Kater L. Heterogeneity of epithelial cells in the human thymus. An ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):227–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00217140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gaudecker B., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Ontogeny and organization of the stationary non-lymphoid cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;207(2):287–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00237813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gaudecker B. Ultrastructure of the age-involuted adult human thymus. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jan 31;186(3):507–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00224939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]