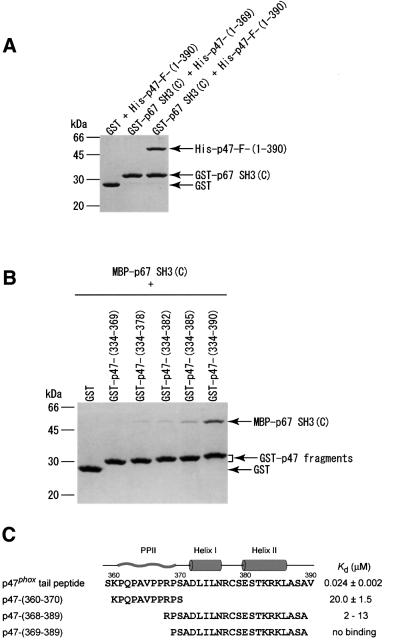
Fig. 2. Effects of the deletions of the C-terminal tail region of p47phox on the interactions with the p67phox SH3(C). The proteins were pulled-down with glutathione beads, and analyzed by SDS–PAGE followed by staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (A) The full-length and the C-terminally truncated form (residues 1–369) of p47phox (with a His tag) were tested for the interaction with the p67phox SH3(C) fused to GST. (B) A series of C-terminally truncated fragments of p47phox fused to GST were tested for the interaction with an MBP-tagged p67phox SH3(C). (C) Amino acid sequence of the p47phox tail peptide, on which the secondary structures in the complex with the p67phox SH3(C) are shown; PPII helix, the first α-helix and the second α-helix. The dissociation constants (Kd) of the p47phox tail peptide and p47-(360–370) for the p67phox SH3(C) were determined by tryptophan fluorescence perturbation. The binding of p47-(368–389) and p47-(369–389) was monitored with the shifts of the [1H,15N]HSQC cross-peaks of the p67phox SH3(C). The analysis of the NMR signals provided a rough estimate of the dissociation constants. The p47phox tail peptide was produced as a GST fusion protein and was cleaved with thrombin, and thus an extra glycine is attached to the N-terminus. The other peptides were prepared chemically, and contain an acetyl group at the N-terminus and an amide group at the C-terminus.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.