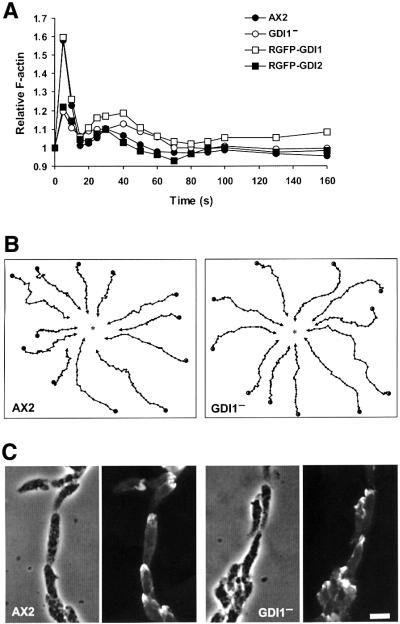
Fig. 6. Actin polymerization and chemotactic response upon cAMP stimulation of aggregation competent cells. (A) F-actin polymerization responses of GDI1– and complementation mutants. The relative F-actin content was determined by TRITC-phalloidin staining of cells fixed at the indicated time points after stimulation with 1 µM cAMP. Each data point represents the average of at least three independent measurements. For the sake of clarity, error bars are not shown. Standard deviations fell between 4% and 11% of the average values. In GDI1– cells, the initial response of actin polymerization and depolymerization was reduced, and was restored after re-expression of GDI1. (B) Chemotactic movement toward a micropipette filled with 0.1 mM cAMP. Cells were starved for 6 h, allowed to sit on a glass coverslip and stimulated with a micropipette filled with 0.1 mM cAMP. Images of chemotaxing cells were captured every 30 s for up to 60 min. DIAS software was used to analyze cell movement and generate the migration paths. The asterisks indicate the position of the micropipette tip. GDI1– cells display an apparently normal chemotactic response. (C) Morphology of aggregation competent wild-type and GDI1– cells. Cells were prepared as in (B), fixed and stained with mAb Act-1 to visualize actin. GDI1– cells are well polarized and build cell streams. Scale bar, 10 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.