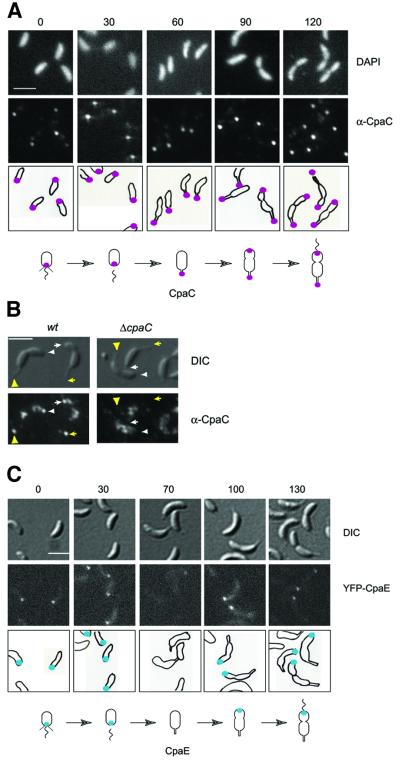
Fig. 2. Cell cycle-dependent polar localization of the CpaC outer membrane channel and the CpaE pilus assembly protein. (A) Subcellular location of CpaC in cells at different stages of the Caulobacter cell cycle was determined using indirect immunofluorescence microscopy. Swarmer cells were isolated and allowed to progress synchronously through the cell cycle. When the cells reached the indicated stages of the cell cycle (0, 30, 60, 90 or 120 min, as indicated above the images) the cells were fixed, treated with lysozyme and the subcellular location of the CpaC outer membrane channel was visualized by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy using affinity-purified CpaC antibodies. A low level of background intracellular signal was observed with a ΔcpaC strain, demonstrating that the polar signal is specific for CpaC (see Figure 3A). Shown are DAPI-stained images of the chromosomal DNA in the cells (upper row), immunofluorescence microscopy images of the cells showing the subcellular locations of CpaC (middle row), and drawings of the location of CpaC within the cells as magenta dots (bottom row). The scale bar in (A–C) represents 2 µm. Shown underneath is a schematic of the location of CpaC during the cell cycle. (B) Location of CpaC at the swarmer cell pole and the tip of the stalk in wild-type and ΔcpaC predivisional cells by immunofluorescence using affinity-purified CpaC antibody. Cells were processed as in (A), except that the lysozyme treatment and DAPI staining were omitted. Shown are images taken by Nomarski differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy (upper panel) and by immunofluorescence microscopy (lower panel). The positions of CpaC in the cell on the left are indicated by arrowheads and in the cell on the right by arrows. The markings point to the location of CpaC at the swarmer cell pole (white) and at the tip of the stalk (yellow). The control experiments on the right show that the polar foci are absent in the ΔcpaC strain. (C) Subcellular location of CpaE in cells at different stages of the Caulobacter cell cycle as determined by direct fluorescence microscopy in a strain expressing YFP–CpaE. Swarmer cells were isolated and allowed to progress synchronously through the cell cycle. When the cells reached the indicated stages of the cell cycle (0, 30, 70, 100 or 130 min, as indicated above the images), samples of cells were withdrawn and placed on a thin layer of agarose, and images were acquired. Shown are DIC images (top panel), fluorescence images (middle panel) and schematics (lower panel) of the subcellular location of YFP–CpaE shown as blue dots. Shown underneath is a schematic of the location of CpaE during the cell cycle.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.