Abstract
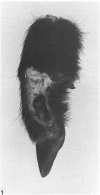
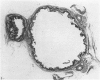
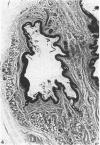
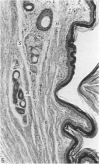
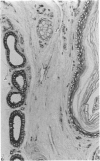
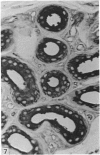
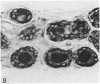
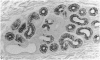
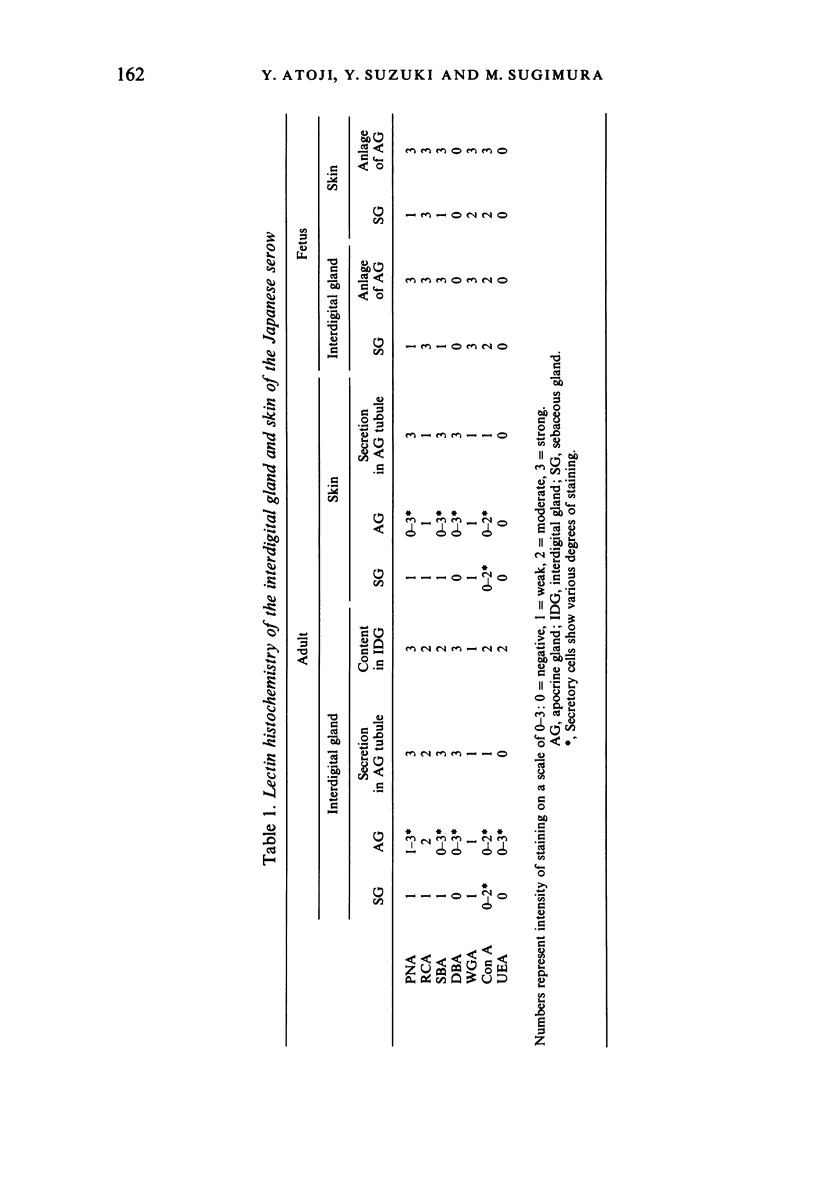
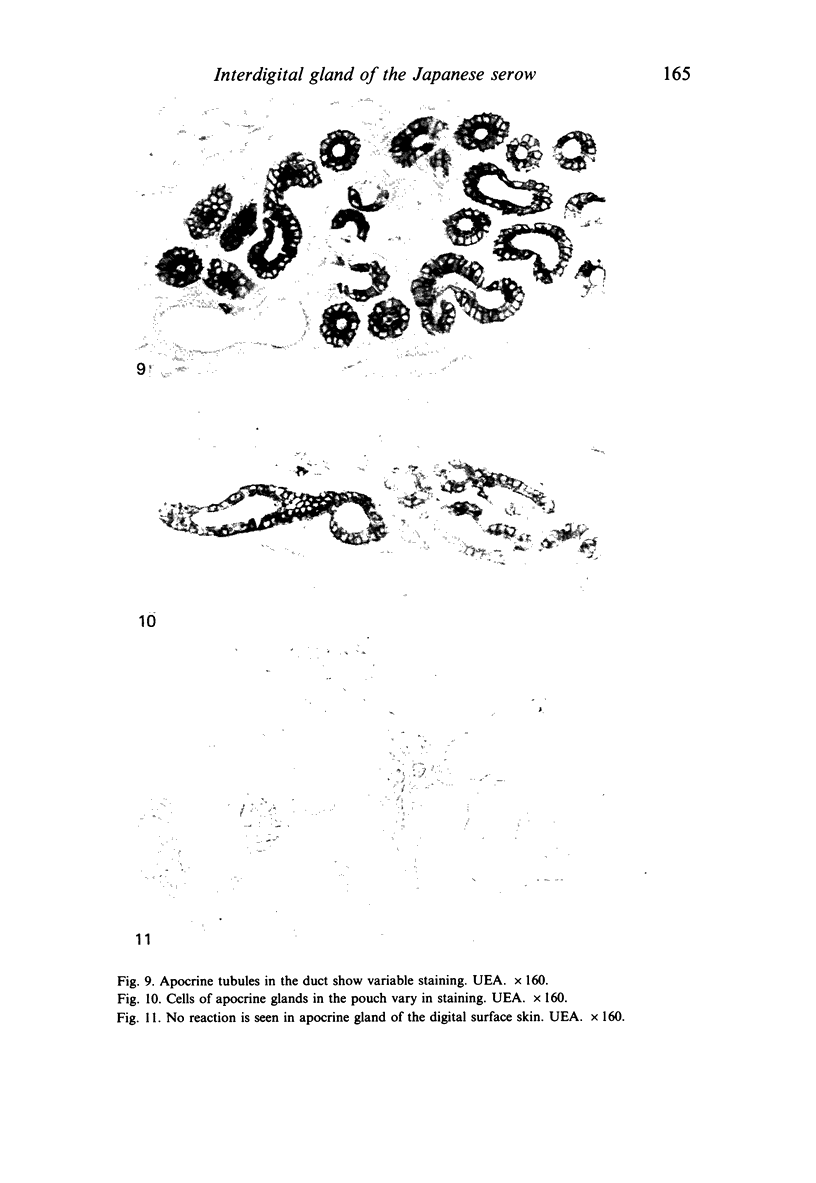
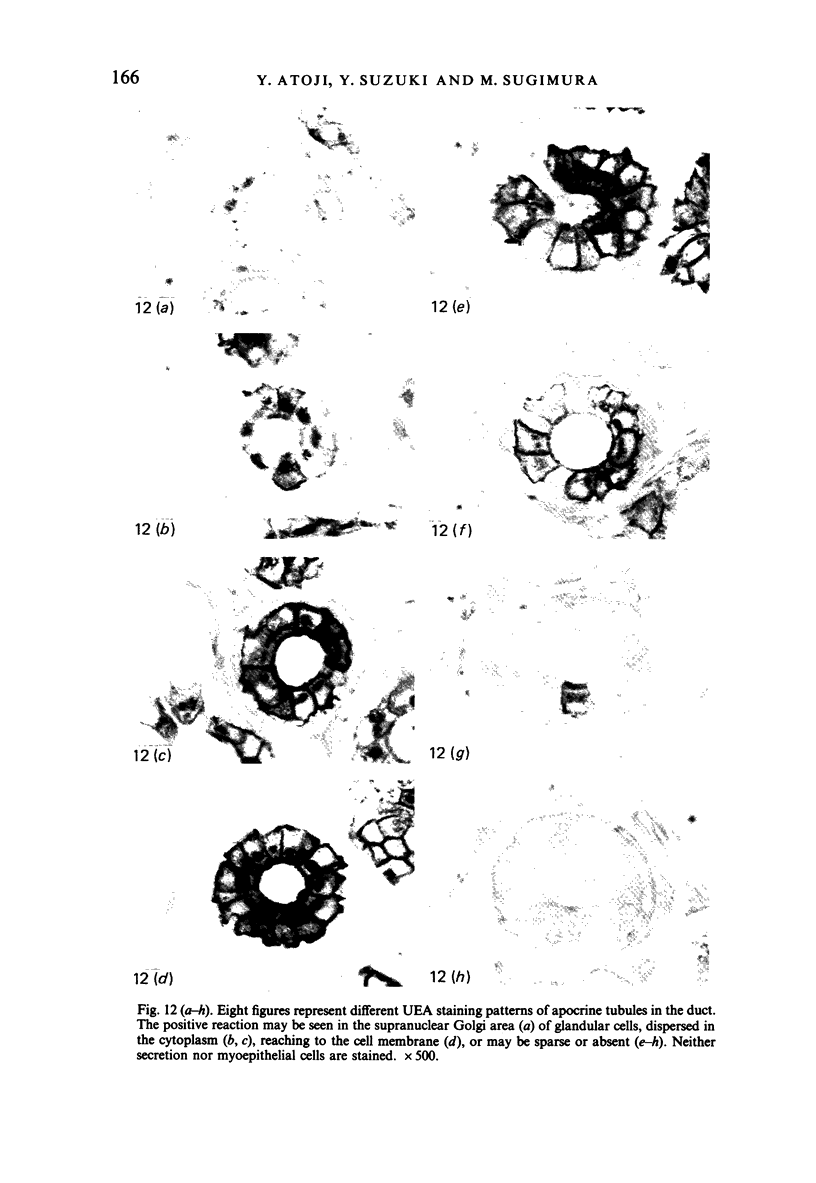
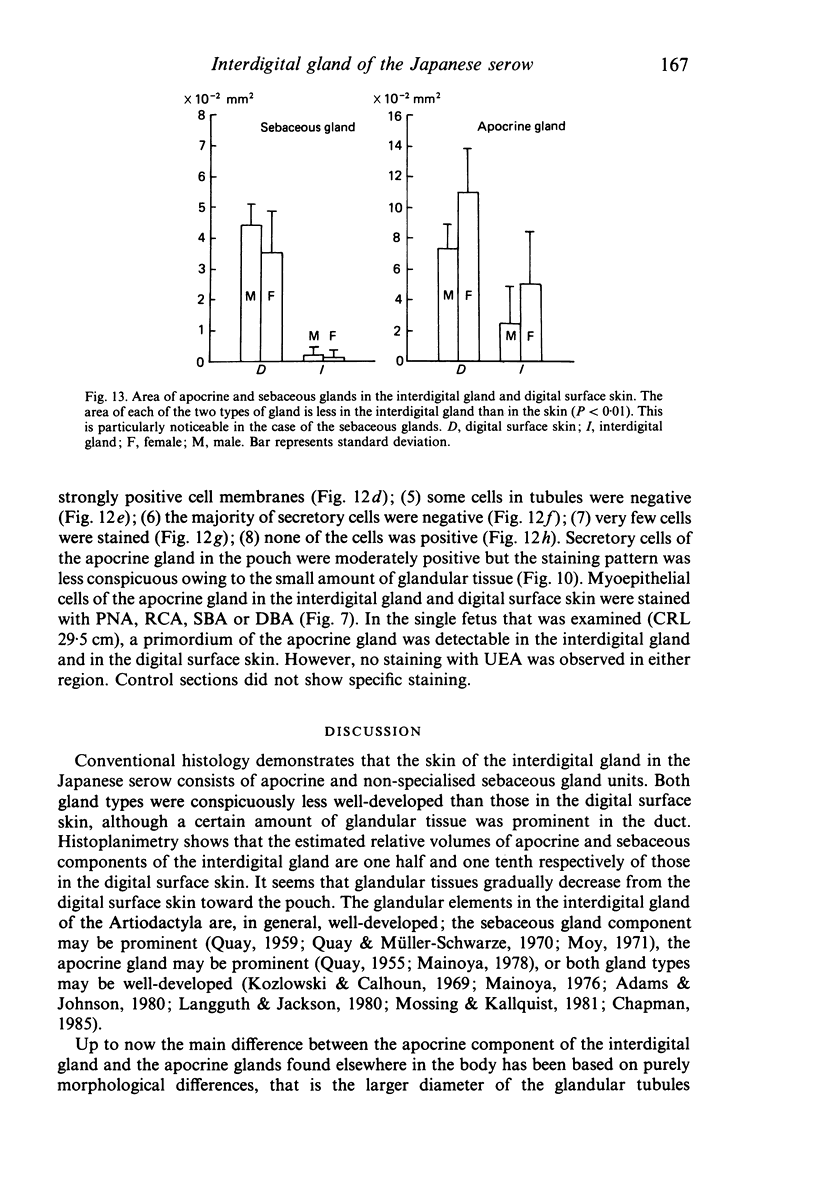
The interdigital gland of the Japanese serow was examined by histological and lectin histochemical techniques. The gland is composed of a thin-walled pouch and a duct. Both regions contain sebaceous and apocrine glands, but the development of each component was significantly less marked than those of the skin in the region. In particular, only a small amount of sebaceous and apocrine glandular elements was found in the pouch, although they were more abundant in the duct. Histochemical staining of the sebaceous and apocrine glands showed similar reactions to six lectins except for UEA in the interdigital gland and digital surface skin. UEA reacted with the apocrine part of the interdigital gland, but not with the gland in the digital surface skin. In addition, tubules in the apocrine gland revealed eight different staining patterns with UEA. These stainings possibly represent a cyclic activity of glandular tubules and suggest that the apocrine portion of the interdigital gland has a different function from that of the body skin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fleischer B. Mechanism of glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Aug;31(8):1033–1040. doi: 10.1177/31.8.6345657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski G. P., Calhoun M. L. Microscopic anatomy of the integument of sheep. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Aug;30(8):1267–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy R. F. Histology of the forefoot and hind foot interdigital and median glands of the pronghorn. J Mammal. 1971 May;52(2):441–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookusa Y. [Histochemical studies of lectin binding pattern in human skin, I. Lectin binding pattern in normal human skin]. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1984 Sep;94(10):1155–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukise A., Meyer W., Ikeda T. Carbohydrate histochemical investigation in the scrotal skin of the common American opossum (Didelphis marsupialis L.). Cell Mol Biol. 1985;31(5):357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]