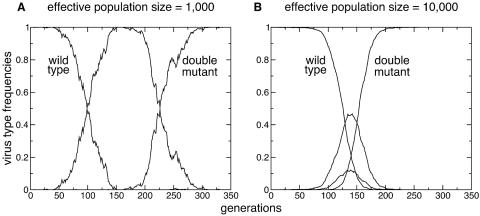
FIG. 2.
Evolution of drug resistance. The homogenous wild-type population is replaced by the resistant double mutant. (A) In a small population of infected cells (Ne = 103), the first single mutation typically rises to fixation before the population acquires the second mutation. (B) In simulations with a larger population of infected cells (Ne = 104), the single mutations are typically both present at the same time. Therefore, recombination can combine the two single mutations and accelerate the evolution of the double mutant.