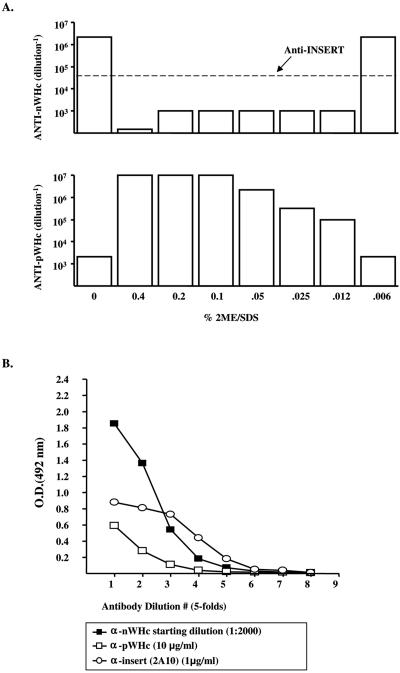
FIG. 2.
(A) Capture ELISAs were designed to detect either WHcAg polypeptide as a marker for expression or WHcAg particles as a marker for assembly in E. coli lysates. An MAb specific for a peptidic epitope on WHcAg is used as the detecting antibody to determine relative expression levels (anti-pWHc; bottom panel). A polyclonal antibody that recognizes only assembled particles (anti-nWHc) is used to determine relative assembly competence (top panel). The capture antibody is a noncompeting MAb specific for a peptidic epitope on WHcAg. Purified malaria-WHcAg hybrid particles were treated with the indicated concentrations of a reducing-denaturing buffer and analyzed in anti-pWHc and anti-nWHc capture ELISAs. A malaria M epitope-specific MAb (2A10) was used to detect the malaria repeat epitope, which was not sensitive to reduction-denaturation. (B) A bacterial lysate of a hybrid M-WHcAg particle was tested in capture ELISAs used to detect assembled particles (anti-nWHc) and levels of protein expression (anti-pWHc) and antigenicity (anti-insert; MAb 2A10). Antibody binding at the indicated dilution is expressed as optical density at 492 nm (OD492).