Fig. 2. PELP1 promotes hypersensitivity to E2 action.
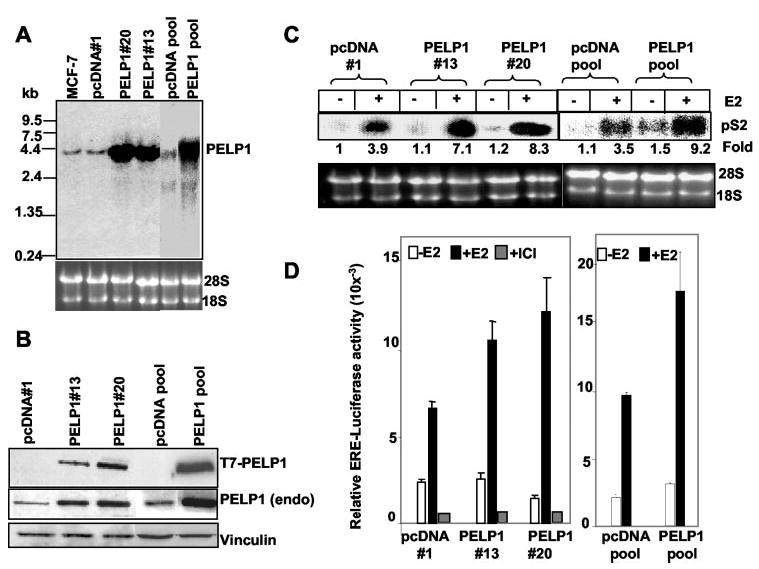
A, total RNA was isolated from pcDNA- and PELP1-expressing clones, and PELP1 expression was analyzed by Northern blotting with a 900-bp fragment coding the N-terminal region of PELP1 as a probe. B, total cell lysates from pcDNA- and PELP1-expressing clones were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-T7 monoclonal antibody, and the membrane was stripped and reprobed using PELP1 antiserum that recognizes endogenous (endo) PELP1. Vinculin was used as a loading control. C, pcDNA- and PELP1-expressing clones were cultured for 48 h in 5% DCC serum and treated with or without E2 for 8 h. Expression of the E2-responsive gene pS2 was analyzed by Northern blotting with a 300-bp pS2 cDNA fragment as a probe. D, pcDNA- and PELP1-expressing clones were cultured for 48 h in DCC serum, transfected with a ERE-luciferase reporter gene, and treated with or without E2 for 24 h. The luciferase activity was then measured. ICI, ICI 182780.
