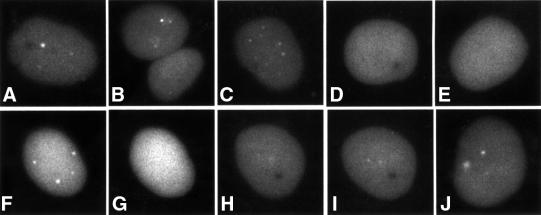
Fig. 2. Detection of parental amplicon genomes at early times after infection. Typical examples of EYFPnlsTetR amplicon-infected cells in the presence of DNA replication inhibitor ACG 90 min after infection. Parental amplicon genomes are detectable as distinct foci (A–C) that are not observed in the presence of tetracycline (D and E). The dots formed in the presence of ACG (F) disappear within 10 min of adding tetracycline (G). Washing to remove the tetracycline allows recruitment of EYFPnlsTetR protein to the dots (H and I, same cell; J is another cell in the same sample after the tetracycline removal).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.