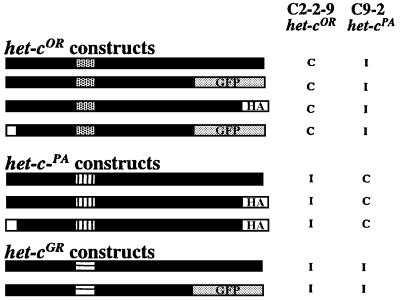
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of epitope-tagged het-c constructs. N-terminal white boxes signify signal peptide deletion constructs. Patterned boxes indicate the het-c allelic specificity domain. GFP-tagged versions of het-cOR and het-cGR included the first 730 amino acids of HET-COR and 727 amino acids of HET-CGR, which are fully functional forms (Saupe et al., 1996). The het-cPA and het-cOR HA-tagged constructs included DNA sequences for the nine amino acid HA-epitope tag fused to the 3′ end of the het-c open reading frame (ORF). Constructs were introduced into standard het-c tester strains C2-2-9 (het-cOR) and C9-2 (het-cPA) (Saupe and Glass, 1997) to test for function. C, compatible transformants; I, incompatible transformants. Differences in phenotype or het-c allelic specificity were not observed when tagged, untagged or het-c signal peptide deletion constructs were introduced into C2-2-9 or C9-2, when using either the gpd promoter or het-c promoter (see Materials and methods).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.