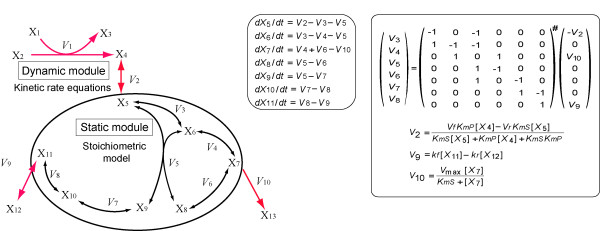
Figure 1.
Summary of the hybrid method. (i) In the dynamic module (V1, V2, V9, and V10), the rate equations provide the reaction rates. (ii) In the static module, the reaction rate distribution (V3, V4, V5, V6, V7, and V8) is calculated from the matrix equation at the right, which corresponds to v = S#b. S# denotes the Moore-Penrose pseudo-inverse of S. (iii) Numerical integration of all the reaction rates (V1-V10) determines the concentrations of the metabolites (X1-X13). The metabolites X5, X7, and X11 are at the boundary.