Abstract
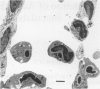
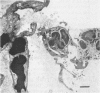
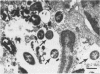
Dose dependent pulmonary lesions of acute bronchopneumonia were induced in male, outbred Swiss Webster mice by intrabronchial inoculation of Pasteurella haemolytica. Five exponential dilutions ranging from 5 x 10(4) to 5 x 10(8) colony forming units per mL (CFU/mL) of Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1 were inoculated into five groups of mice. Mice were killed by cervical dislocation 24 hours postinoculation. Pulmonary lesions occurred in mice of all five groups, however, 5 x 10(7) CFU/mL was the minimal dose which consistently produced lesions. Focal parenchymal necrosis, suppurative bronchiolitis, and flooding of interalveolar septa and alveoli by edema fluid, fibrin, neutrophils and macrophages, were observed microscopically. We conclude that outbred Swiss Webster mice can be used as a model for the study of selected disease mechanisms of acute lung inflammation and that this model may be used to determine some of the pathogenic mechanisms involved in the development of pulmonary lesions in bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames T. R., Markham R. J., Opuda-Asibo J., Leininger J. R., Maheswaran S. K. Pulmonary response to intratracheal challenge with Pasteurella haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Oct;49(4):395–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. G., Mtero S. S., Niderbuhl C. J., Collins F. M. Fate of Pasteurella hemolytica in conventionally raised and germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):202–207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.202-207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Renshaw H. W., Martens R. J., Livingston C. W., Jr Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin: chemiluminescent responses of peripheral blood leukocytes from several different mammalian species to leukotoxin- and opsonin-treated living and killed Pasteurella haemolytica and Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chengappa M. M., Carter G. R., Chang T. S. Hemoglobin enhancement of experimental infection of mice with Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Aug;44(8):1545–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. B., Wells P. W. A mouse model of Pasteurella haemolytica infection and its use in assessment of the efficacy of P haemolytica vaccines. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Sep;27(2):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H. Pasteurella haemolytica and respiratory disease in cattle. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1979;(83):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Thomson R. G., Wilkie B. N. Pulmonary lesions induced by Pasteurella hemolytica in cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Apr;41(2):219–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour M. I., Wathes C. M., Taylor F. G. The airborne survival of Pasteurella haemolytica and its deposition in and clearance from the mouse lung. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Feb;21(4):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90008-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritani M., Nakazawa M., Oohashi S., Yamada Y., Haziroglu R., Narita M. Immunoperoxidase evaluation of pneumonic lesions induced by Pasteurella haemolytica in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Sep;48(9):1358–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilwig R. W., Songer J. G., Reggiardo C. Experimentally induced pneumonic pasteurellosis: dose-response relationships and protection against natural reinfection in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2585–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jian Z., Alley M. R., Manktelow B. W. Experimental pneumonia in mice produced by combined administration of Bordetella parapertussis and Pasteurella haemolytica isolated from sheep. J Comp Pathol. 1991 Apr;104(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(08)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaehler K. L., Markham R. J., Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W. Evidence of species specificity in the cytocidal effects of Pasteurella haemolytica. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):615–616. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.615-616.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVey D. S., Loan R. W. Antibody complement-dependent bacteriolysis in experimentally induced pasteurellosis in mice. Am J Vet Res. 1989 May;50(5):762–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morck D. W., Costerton J. W., Bolingbroke D. O., Ceri H., Boyd N. D., Olson M. E. A guinea pig model of bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Jan;54(1):139–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace L. W., Kreeger J. M., Bailey K. L., Turnquist S. E., Fales W. H. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in calves experimentally infected with Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jan;35(3-4):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: model for Pasteurella haemolytica- and Pasteurella multocida-induced pneumonia in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2532–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH G. R. Experimental infections of Pasteurella haemolytica in mice and their use in demonstrating passive immunity. J Comp Pathol. 1958 Oct;68(4):455–468. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(58)80051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoo M. K. Experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: a review. Vet Rec. 1989 Feb 11;124(6):141–144. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.6.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessman G. E. Susceptibility of mice, guinea pigs and hamsters to challenge with Pasteurella hemolytica and its enhancement by microbial polysaccharides and related compounds. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):421–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley L. O., Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Ames T. R., Kannan M. S. Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and bovine respiratory disease: pathogenesis. J Vet Intern Med. 1992 Jan-Feb;6(1):11–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1992.tb00980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]