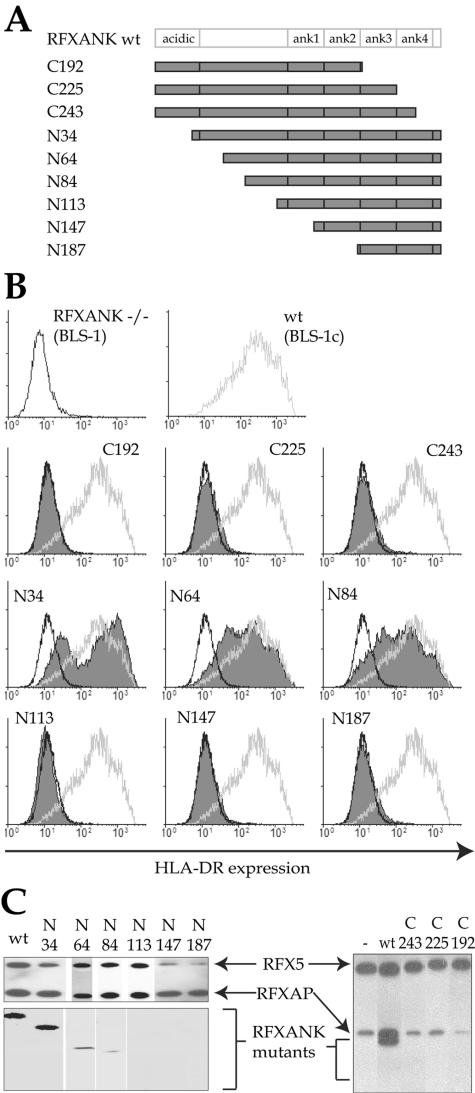
FIG. 1.
Analysis of RFXANK deletion mutants. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type RFXANK and the deletion mutants used in this study. The C-terminal acidic domain and the N-terminal ankyrin repeats are indicated. The names of the mutants correspond to the end points of C- and N-terminal deletions. (B) FACS analysis of cell surface expression of HLA-DR in the BLS-1 (RFXANK−/−) B-cell line transfected stably with wild-type (wt) (BLS-1c) or mutant RFXANK constructs. The BLS-1 and BLS-1c profiles are included as a reference. Open black profiles correspond to BLS-1; open gray profiles correspond to BLS-1c; filled profiles represent cells complemented with the deletion mutants. (C) Promoter pull-down experiments performed with extracts prepared from BLS-1 cells or BLS-1 cells transfected with the indicated constructs. MHC-II enhanceosomes were assembled on HLA-DRA promoter fragments, purified, and analyzed for the presence of the three RFX subunits by Western blotting. Equal amounts of extract were used for each pull down. A partial RFX complex containing only RFX5 and RFXAP was pulled down in the absence of RFXANK (right, lane −). Functional RFXANK mutants (N34, N64, and N84) are integrated into this complex, while nonfunctional mutants (N113, N147, N187, C243, C225, and C192) are not.