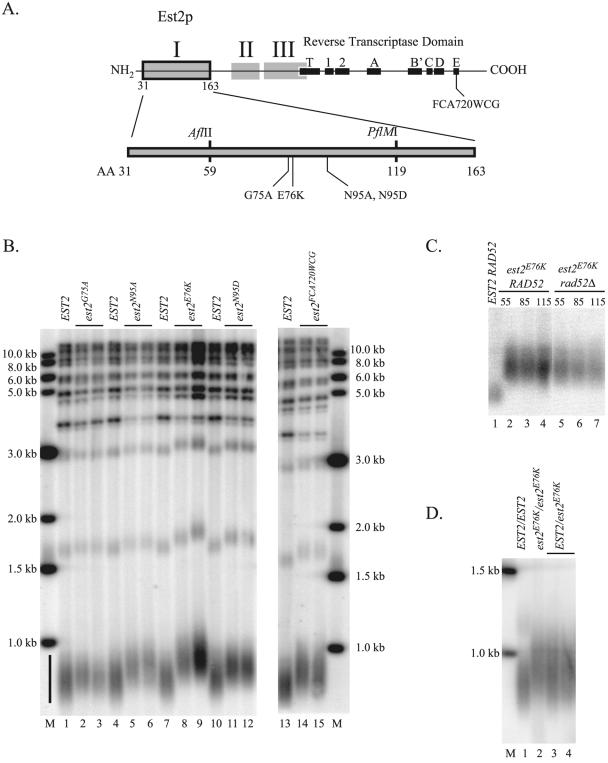
FIG. 1.
Mutations in region I of Est2p cause telomere lengthening. (A) Map of functional regions of Est2p. Top: map of Est2p primary sequence indicating the locations of the reverse transcriptase domain and three N-terminal regions that are essential for telomere maintenance in yeast. The location of the est2FCA720WCG mutation is indicated (42). Bottom: detailed map of region I of Est2p. The locations of mutations that result in telomere lengthening are indicated (G75A, glycine 75 to alanine; E76K, glutamic acid 76 to lysine; N95A, asparagine 95 to alanine; N95D, asparagine 95 to aspartic acid). Unique AflII and PflMI restriction sites were used in a gap repair strategy to identify additional alleles of est2 with the long-telomere phenotype (see text). (B) Telomere length is increased in strains expressing plasmid-borne est2LT alleles. All strains are derived from YKF120 (est2::HIS3) and carry plasmids expressing wild-type or mutant protein A-tagged EST2. Genomic DNA from strains expressing ProA-EST2 (lanes 1, 4, 7, 10, and 13), ProA-est2G75A (lanes 2 and 3), ProA-est2N95A (lanes 5 and 6), ProA-est2E76K (lanes 8 and 9), ProA-est2N95D (lanes 11 and 12), or ProA-est2FCA720WCG (lanes 14 and 15) was digested with PstI, separated in a 1.2% agarose gel, blotted, and probed with telomeric DNA. The black bar indicates a smear of fragments derived from the 2/3 of yeast chromosomes that contain a subtelomeric Y′ element. Upper bands derive from non-Y′ telomeres and tandemly repeated Y′ elements. The sizes of marker bands (M) are indicated. (C) Telomere lengthening caused by est2E76K is stable and independent of Rad52p. Strains YKF120 (est2::HIS3 RAD52; lanes 2 to 4) and YKF114 (est2::HIS3 rad52::LEU2; lanes 5 to 7) were transformed with pKF410-est2E76K, a low-copy-number vector expressing the ProA-tagged est2E76K allele. Transformants were restreaked once on media lacking uracil, and a single colony was grown to saturation in 5 ml liquid media lacking uracil. Liquid cultures were serially diluted 1,000-fold and allowed to regrow to saturation a total of 10 times. Genomic DNA was harvested from samples corresponding to approximately 55 (lanes 2 and 5), 85 (lanes 3 and 6), and 115 generations (lanes 4 and 7) after transformation of the mutant allele, digested with PstI, separated by gel electrophoresis, and probed with a telomeric probe. The control lane contains DNA harvested from YKF120 (est2::HIS3 RAD52; lane 1) transformed with a plasmid expressing protein A-tagged wild-type EST2 (pKF410) and grown for a minimum of 115 generations. Only the telomeric smear corresponding to Y′ chromosomes is shown. (D) The est2E76K allele is semidominant to the wild type. DNA from diploid strains EST2/EST2 (DKF206; lane 1), est2E76K/est2E76K (DKF207; lane 2), and EST2/est2E76K (DKF208; lanes 3 and 4) was digested with PstI and subjected to Southern blotting as described above. The sizes of marker bands are indicated (M).