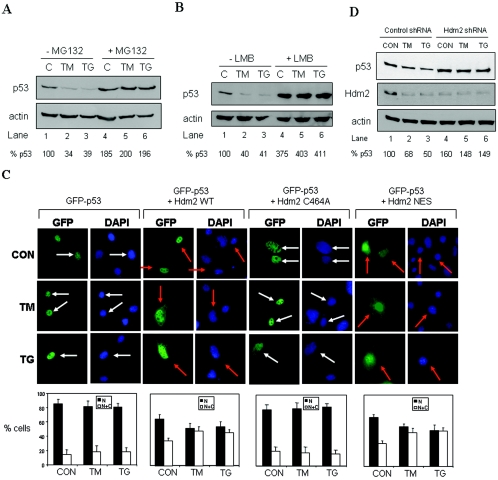
FIG. 1.
Hdm2-mediated nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and degradation of p53 in ER-stressed cells. (A and B) A549 cells were pretreated with either 10 μM MG132 (A, lanes 4 to 6) or 4 nM LMB (B, lanes 4 to 6) for 4 h prior to treatment with 1 μM TG (lanes 2 and 5) or 10 μg of TM/ml (lanes 3 and 6) for 2 h. Protein extracts were subjected to Western blotting with anti-p53 (DO-1) Ab (top panel) and anti-actin Ab (bottom panel). The p53 protein levels were normalized to actin levels (% p53) by using Scion Image 2.0 software. (C) Subcellular localization of GFP-p53. GFP-p53 WT cDNA (0.25 μg) was transiently transfected in the absence or presence of an equal amount of Hdm2 WT, Hdm2 NES, or Hdm2 C464A cDNA into 2KO cells. After 24 h, the cells were left untreated or treated with either 10 μg of TM/ml or 1 μM TG for 4 h, and GFP-p53 localization was examined by fluorescence microscopy. The nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining. White arrows indicate nuclear localization of GFP-p53 only, whereas orange arrows indicate both cytoplasmic and nuclear localization. The quantification of GFP-p53 localization is described in Materials and Methods. Cells with predominantly nuclear p53 are represented by the black bars, whereas cells with p53 both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm are represented by the white bars. Values are means ± the standard deviation (SD) from three experiments. (D) Inhibition of Hdm2 expression by shRNA. A549 cells subjected to Hdm2 silencing by shRNA (see Materials and Methods) were treated with either 10 μg of TM/ml or 1 μM TG for 2 h. Protein extracts (50 μg) were immunoblotted with anti-p53 (DO-1) Ab (top panel), anti-Hdm2 Ab (middle panel), or antiactin Ab (bottom panel).